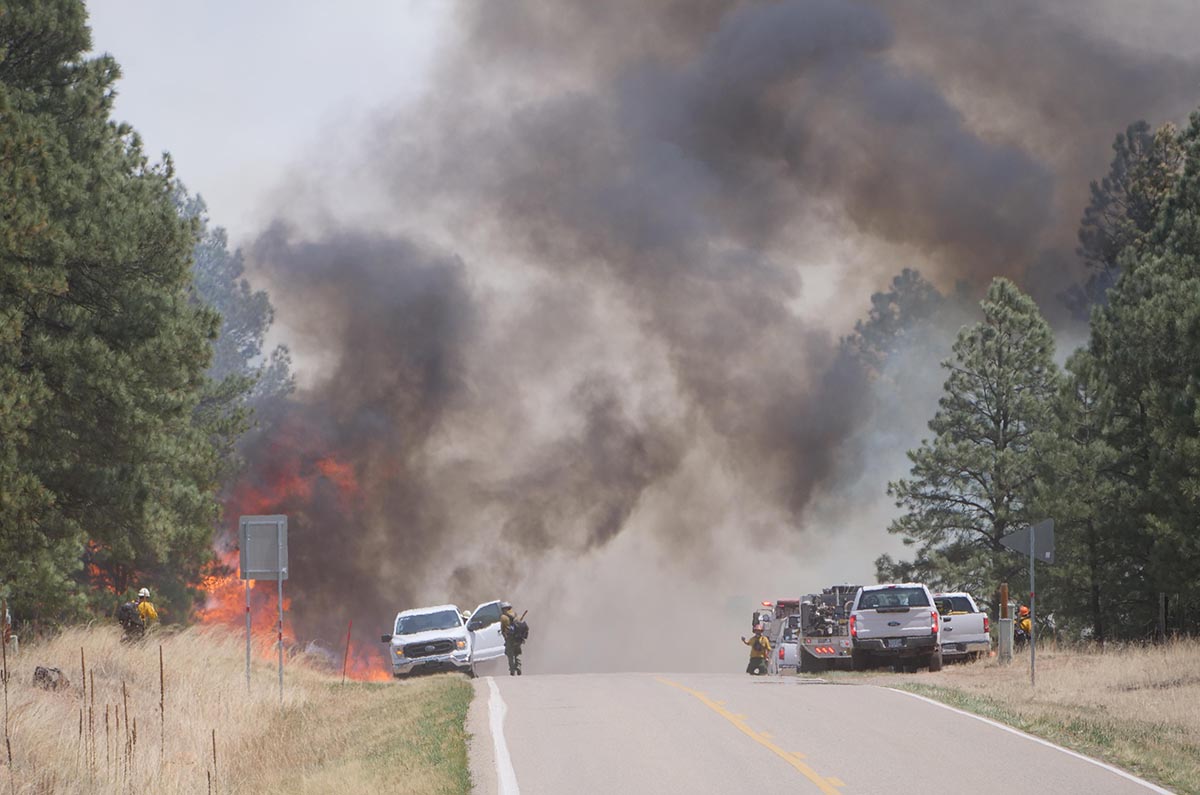
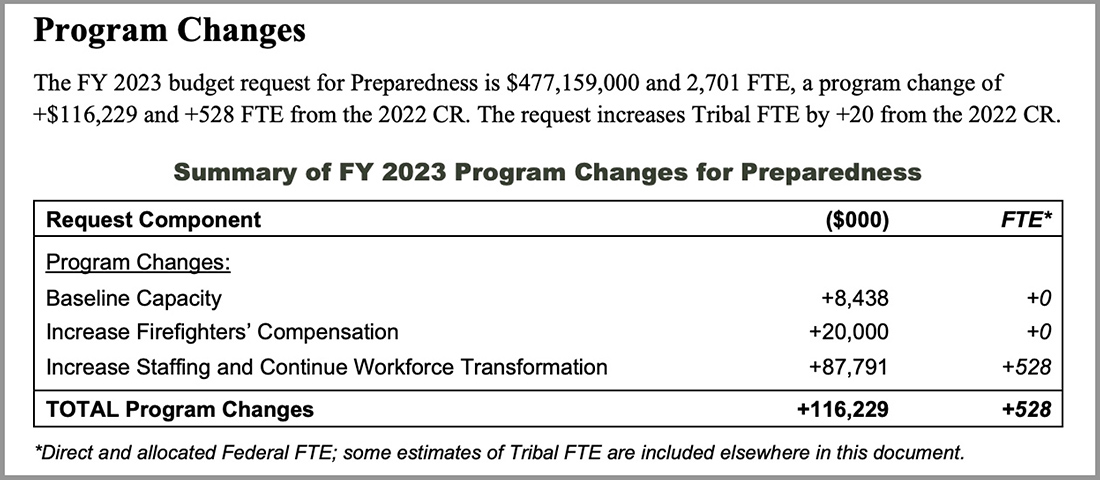
Federal wildland fire funding may increase by nearly 25 percent in 2024 if President Biden’s budget priorities are adopted by Congress. The budget, released March 9, reflects firefighters’ concerns and a rising political commitment to face increasingly complex wildfire conditions.
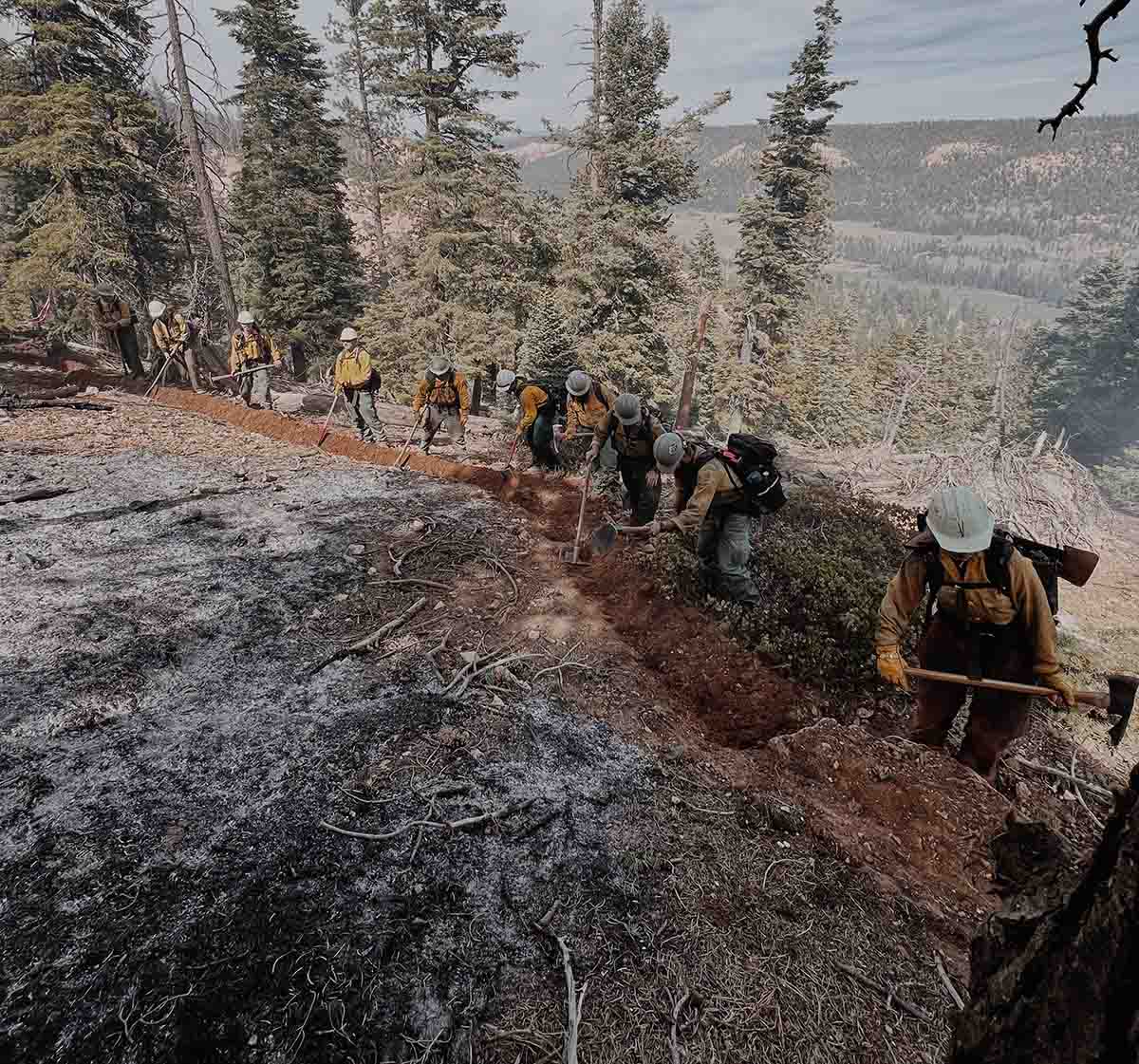
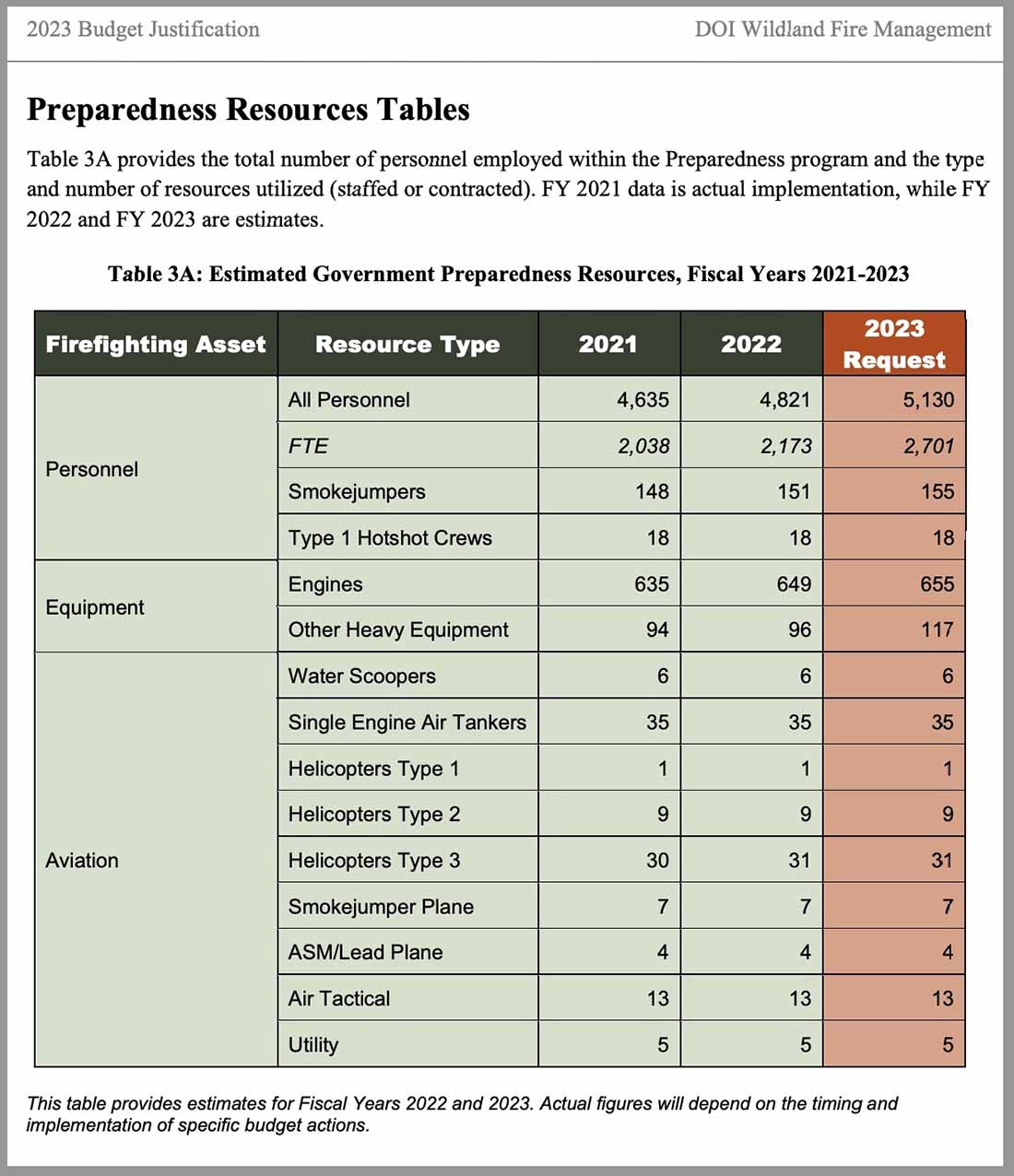
Initiatives include a long-term fix for wildland firefighter pay equity, an 8 percent increase in the number of federal and Tribal firefighters, and expansion of prior commitments to interagency response and research, fuels management, aviation and remote sensing initiatives, and community-based prevention programs.
T he summary fact sheet released by the Office of Management and Budget has a single mention of wildfires, woven into a $24 billion investment to “build communities’ resilience to floods, wildfires, storms, extreme heat, and drought brought on by climate change.”
he summary fact sheet released by the Office of Management and Budget has a single mention of wildfires, woven into a $24 billion investment to “build communities’ resilience to floods, wildfires, storms, extreme heat, and drought brought on by climate change.”
Wildfire and wildland fire management funding in the 2024 budget appear in joint and specific releases by the lead agencies with federal wildland fire management responsibilities. The U.S. Department of Agriculture proposes a 28 percent increase and the Department of the Interior proposes a 21 percent increase over 2023 funding.
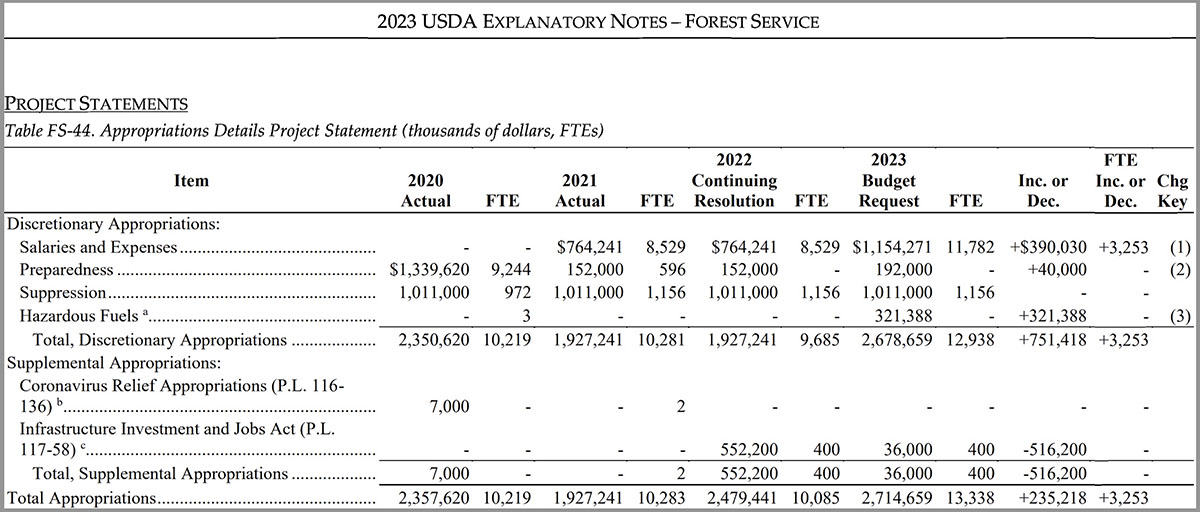
News releases from both departments note the priority for funding the proposed raises in base pay for federal and tribal firefighters. The budget summary notes that funding will pay for fuels as well as fire management. The proposal calls for “More than $4.2 billion for the U.S. Departments of Agriculture and the Interior wildland fire and hazardous fuels management” that will “implement comprehensive workforce reform, including increased firefighter pay, additional firefighting capacity, enhanced mental and physical health support, and improved housing options for firefighters.”
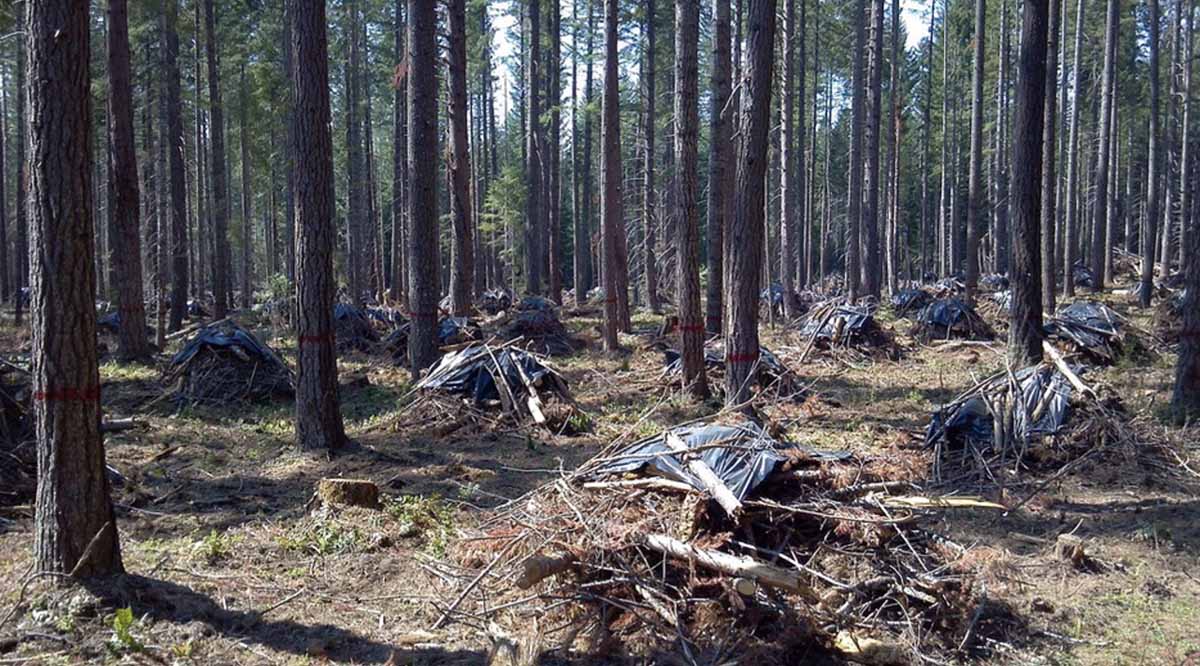
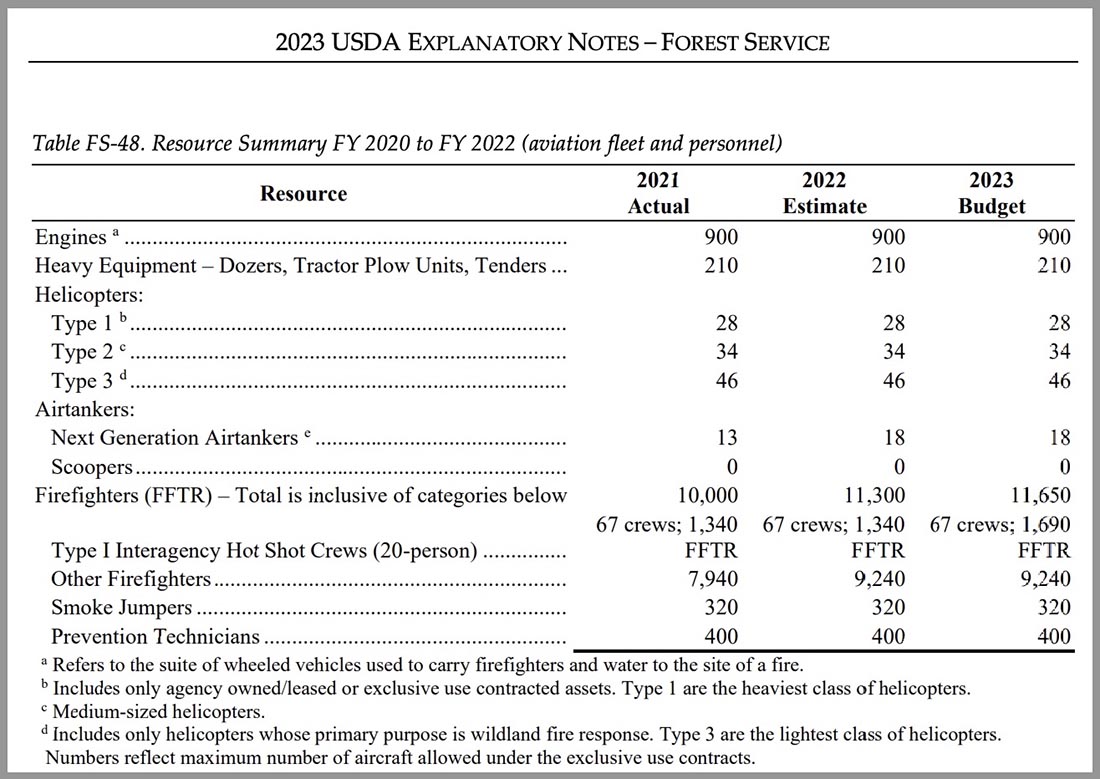
As detailed in a March 9 USDA release, “The budget includes increases of $180 million for USDA and $72 million for DOI to raise base pay for Federal and Tribal wildland firefighters, with additional premium pay costs covered out of funding requested for suppression operations.” The USFS Explanatory Notes page for the 2024 budget includes additional details and annual performance indicators. One indicator of note for 2022: on page 233, it’s reported that nearly 3 million acres of fuels treatments were accomplished, with 57 percent using prescribed fire despite a prescribed fire pause (followed by the release of the National Prescribed Fire Program Review) put in place after prescribed fire escapes in New Mexico. The 2024 budget increases hazardous fuels targets to 4 million acres.
The DOI release expands on the appropriations request: “The President’s 2024 Budget proposes legislation and funding to implement significant reforms to increase the Nation’s investment in the wildland fire management workforce. The cornerstone of these long-term reforms is a permanent increase in pay. The Administration proposes legislation to establish a special base rate salary table for wildland firefighters, create a new premium pay category that provides some additional compensation for all hours a wildland fire responder is mobilized on an incident, and establish a streamlined pay cap that provides waiver authority to the Secretary using specific criteria.”
The pay-raise focus has garnered support from the National Federation of Federal Employees. In a March 13 release, NFFE President Randy Erwin praises President Biden for “taking this critical step in addressing the wildfire crisis and improving the lives of federal wildland firefighters across the country.”
Erwin noted that pay reforms will “help recruit and retain skilled personnel … While there is still much work to do to ensure our wildland firefighting workforce has the resources to be sustainable in the coming years, I am proud that our members are seeing results from their advocacy.”
Approval of the budget faces the challenge of a divided Congress. A Republican-majority House may push back against the overall budget, resulting in a flat-lined continuing resolution in place of an approved 2024 budget. Additionally, implementation may be shaped by legislation that may result from reports and recommendations of the Wildland Fire Mitigation and Management Commission. The commission’s final call for recommendations from the public (including firefighters) closes on March 22.