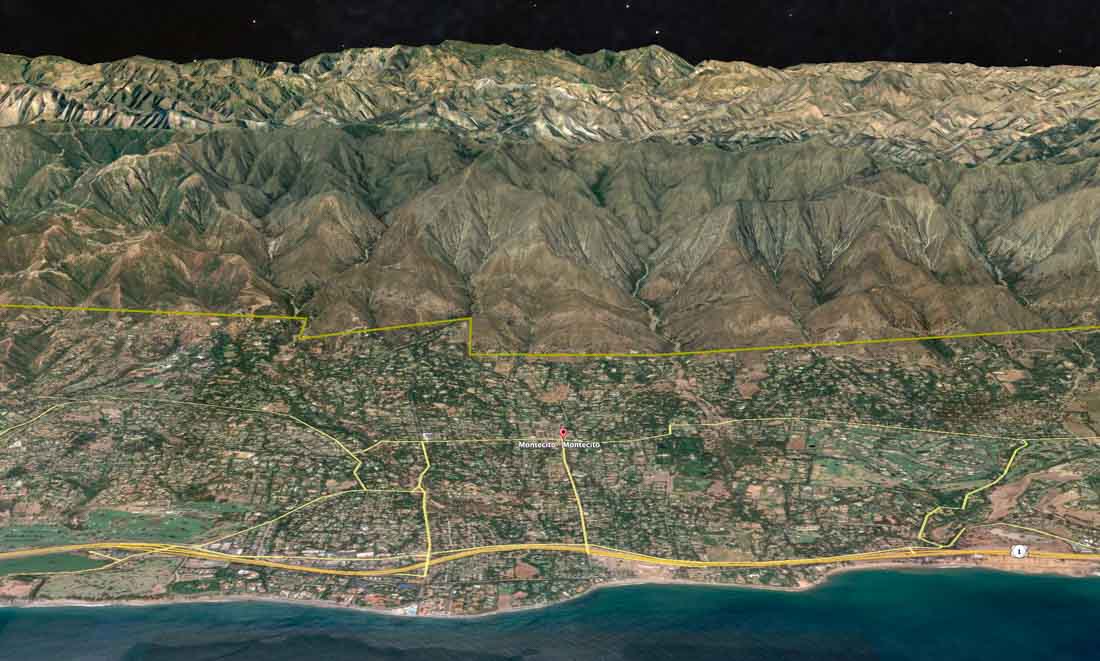
In December, 2017 the Thomas Fire burned over 281,000 acres and 1,000 homes in Ventura and Santa Barbara Counties in Southern California. But in Montecito, with a wildland-urban interface stretching for five miles along the Los Padres National Forest boundary, only seven primary residences were destroyed. Considered a success story, this result is due to many factors, including the fact that homeowners and firefighters had days to prepare for the fire entering the city, which meant that firefighters did not have to make a choice between helping residents to evacuate or protecting homes. This is in stark contrast to last November’s Camp Fire that raced into Paradise, California within a couple of hours after being ignited by a PG&E power line. In that case firefighters did not have the luxury of suppressing the fire as it burned homes; they had to concentrate on helping residents evacuate and saving lives.
But another important factor that helped to reduce the number of homes destroyed in Montecito in 2017 was the pre-fire mitigation work that had been ongoing in the community for two decades.
After the fire the Montecito Fire Protection District sought to document and understand the confluence of social, ecological, and biophysical factors associated with implementing fire adaptation activities and how they affected the outcome of the Thomas Fire in their community.
The findings in this study should be considered by all communities in a fire-prone environment. Cities that resist mitigation efforts such as constructing fuel breaks, enacting FireWise building codes, spacing homes more than 10 to 20 feet apart, planning for evacuations, and being proactive in protecting their residents long before smoke is in the air, are doomed to a very unpleasant and rude awakening one day. It is not IF a fire will impact their community, it is WHEN.
Below are excerpts from the Montecito study, conducted by Crystal A. Kolden and Carol Henson. The entire report is open source.
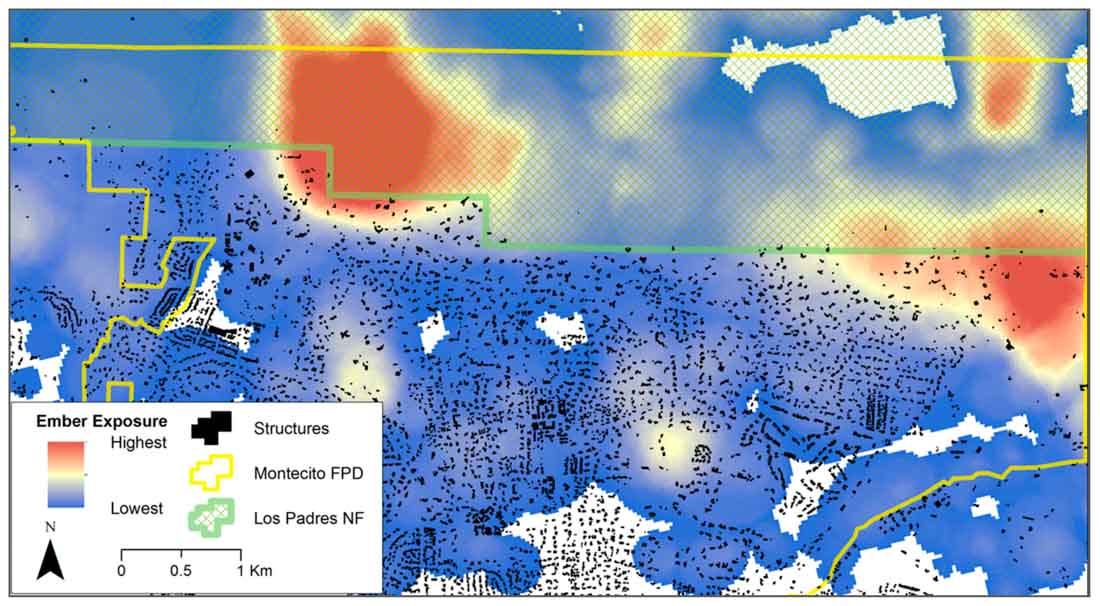
…Here, we document both the social and the biophysical vulnerability reduction strategies taken by the community of Montecito, California in Santa Barbara County, USA, prior to the 2017 Thomas Fire, and how those strategies translated into outcomes. Montecito is one of the many communities in the United States that has been repeatedly exposed to wildfires over the last several decades, with multiple disastrous events . As such, the Montecito Fire Protection District (MFPD) embarked on an effort to reduce wildfire vulnerability in the community two decades ago. That effort was subsequently tested in the December 2017 Thomas Fire, which consumed over 1000 homes and became the largest wildfire in contemporary California history for several months until it was surpassed in 2018. Most of the homes were consumed at the outset of the Thomas Fire on days when strong downslope winds (i.e., Santa Ana and Sundowner winds) prevailed, and extreme fire behavior including long runs and long-range spotting, occurred, overwhelming fire suppression efforts. By contrast, Montecito experienced relatively little infrastructure damage from the Thomas Fire, despite similar conditions, including extreme fire behavior and the presence of Sundowner winds on the day the fire beset the community (16 December 2018).
Over the 20-year period between 1999 and 2018, the MFPD expended approximately $1.76 million (mill) USD ($2 mill USD adjusted for inflation to 2018) on wildfire vulnerability reduction activities (Figure 2). We include 2018 here as these are fiscal year totals, where the fiscal year ends June 30 of the year listed, so the Fiscal Year 2018 (FY2018) expenditures were primarily expended in autumn 2017, prior to the December ignition of the Thomas Fire (this also contributes to reduced FY2018 expenditures relative to prior years). When adjusted for inflation, it is clear that funding was inter-annually variable, but generally increasing over time (Figure 2).
Most of the activities undertaken by MFPD addressed more than one component of the vulnerability triangle (i.e., exposure, sensitivity, and adaptive capacity).
- Any action that specifically identified geospatial patterns of exposure to wildfire (e.g., defensible space surveys), or was designed to reduce direct exposure to wildfire (e.g., defensible space improvements, roadside fuel reduction) addressed exposure vulnerability.
- Any action that specifically identified populations in the community that are more sensitive to the negative ramifications of wildfire and determined population-specific actions designed to mitigate those ramifications addressed sensitivity vulnerability.
- Any action that increased the ability of the community to respond to wildfire and reduce the negative ramifications developed adaptive capacity.
An action such as hiring a Wildland Fire Specialist, whose primary position is to build relationships with community members and facilitate programs to reduce vulnerability, addressed all three components of vulnerability.
Evacuation and ingress/egress issues were key elements of two other activities undertaken by MFPD prior to 2017.
First, MFPD improved ingress/egress and evacuation and fire suppression effectiveness by delineating pre-attack zones across the community in their wildland fire initial attack plan. MFPD utilized these pre-attack zones (which are essentially sub-units of the community that were delineated prior to firefighters attacking a future, hypothetical wildfire) in their community education efforts, planning process, and printed high-resolution paper maps of each zone that were pre-packed in a portable file box for distribution to non-MFPD fire suppression resources in the event of a wildfire. Nine of the interviewees noted the utility of these maps in facilitating greater life safety for firefighters and increased suppression effectiveness, because the maps were able to help resources not familiar with the area to navigate the community safely and quickly and find the pre-designated water sources and equipment staging areas in Montecito, which were also marked on the map.
Second, while MFPD implemented several new fire codes focused specifically on structures (e.g., banning cedar shakes for roofing and siding, requiring boxed eaves), a new requirement for wider driveways focused on reducing exposure through improved evacuation, and increasing adaptive capacity by facilitating firefighter safety during fire suppression activities and post-fire clean up. In Montecito, as in many WUI communities, many of the homes are located at the end of long (>100 m), narrow, winding driveways that terminate at garages. Increasing driveway width and turnaround space supports larger fire apparatus and other large equipment allowed firefighters access these areas, and safely use a tactic referred to as “fire following.” Fire following is frequently used during extreme conditions, wherein firefighters (1) prepare homes to resist an oncoming wildfire, (2) retreat from the home or neighborhood when extreme fire behavior and direct flames from the fire front threaten their life safety, and then (3) “follow” behind the flaming front and re-engage with the home or in the neighborhood. During this re-engagement, they focus on extinguishing portions of the structure that are on fire, extinguishing spot fires on the property, remove flaming debris from structures (e.g., flaming palm fronds on the roof or deck), and wetting down vegetation if there are additional threats for re-ignition (e.g., additional spot fires). Fire following depends on firefighters being able to safely navigate to a home and turn around so that they can evacuate rapidly if needed; driveway design is paramount to this dependency.
The effectiveness of fire suppression efforts was directly supported by the pre-fire vulnerability reduction efforts undertaken by MFPD. Interviewees noted that they were able to use fire following tactics because homes were fire-resistant, giving firefighters time to engage and remove flammable debris before a structure became fully involved with fire. Firefighters also described being able to engage because most homes had sufficient defensible space to make it safe for them to do so, without fear of entrapment. This was of particular concern due to entrapment of firefighters that occurred on the nearby Jesusita Fire in 2009, which was associated with lack of defensible space and evacuation routes.
Interviewees also noted that suppression effectiveness was amplified by the reduction of roadside fuels, which allowed them to conduct backfiring operations along some parts of the road system and hold the fire along other segments. Interviewees described the difference between other portions of the Thomas Fire in Santa Barbara County, where heavy roadside vegetation created a “tunnel effect” that inhibited large fire apparatus passage (leading to over a dozen homes destroyed in one nearby canyon), and Montecito, where roadside clearance eliminated vegetation tunnels and facilitated two large city fire apparatus being able to pass each other on narrow roads. Videos taken by some interviewees further demonstrated how such clearance improved firefighter safety given the low visibility created by heavy smoke. Several firefighter fatalities in the US have been attributed to exiting the roadway due to lack of visibility in smoky conditions.
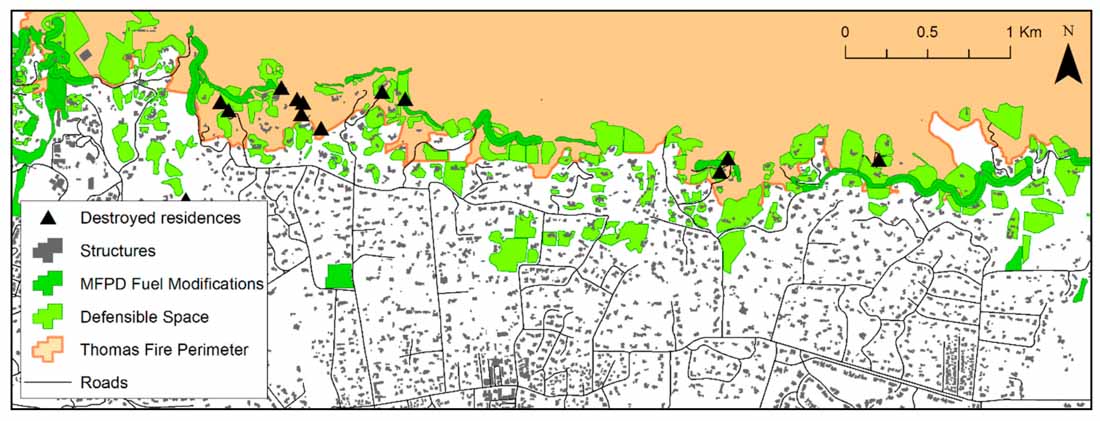
Both defensible space and roadside fuel treatments were supplemented by the community fuel treatments implemented by MFPD, which served to “link” together with the fuel reductions undertaken by residents and along roadways. All but one interviewee described this network of fuels reduction as being vital to effective suppression efforts and structure protection, specifically because it allowed firefighters to engage the fire safely. Of the seven primary residences destroyed in Montecito, two were located below a ‘gap’ in the fuel treatment network, and the loss of the remaining dwellings was primarily attributed to the presence of fuels immediately adjacent to the structure, and inaccessibility for firefighters to support the fire following tactic. These losses were attributed to fire exposure that was not mitigated.

All I want to know,is this,California needs ( and starting many,many years ago) a plan to start Prescibed fire councils all over the state.It is the very best forest management tool,going back to when native americans utilized this practice.It is needed today,more than ever..well due to climate change,and to benefit ‘fireprone ecology.