 In December of 2017, the Federal Emergency Management Agency Administrator requested the Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology research new and emerging technology that could be applied to wildland fire incident response, given the loss of life that occurred in California during the fall of 2017 in Santa Rosa and Ventura.
In December of 2017, the Federal Emergency Management Agency Administrator requested the Department of Homeland Security Science and Technology research new and emerging technology that could be applied to wildland fire incident response, given the loss of life that occurred in California during the fall of 2017 in Santa Rosa and Ventura.
The project team identified three overarching conclusions that represent consistent themes captured throughout the course of the table top exercises and expert engagements.
- Time Criticality of WUI Fire Incidents: WUI fire incidents require immediate protective and response actions to save lives. The conflagration created when a wildland fire enters populated areas is unpredictable and can rapidly devastate these areas, threatening lives. Interventions and solutions that improve decision making and response in the initial minutes of a WUI fire are vital.
- Available Technology Solutions Exist: There exist available technologies (both government and commercial), which—if implemented—could immediately help emergency responders reduce the number of lives lost during WUI fire incidents. In particular, these technologies could immediately support ignition detection, fire tracking, public information and warning, evacuation, and responder safety. Improving capabilities in other elements of the WUI response (i.e. preparedness and critical infrastructure) may require investing in adaptable or developable solutions that are not immediately available.
- Public Education and Preparedness Measures are Vital: Public education and preparedness are essential to reducing the number of lives lost to WUI fire incidents. There is no solution more effective than preventing an ignition in the first place and ensuring the at-risk communities are prepared at the grassroots level to face wildland fire dangers.
The principal conclusions of this project are distilled into a set of seven key findings. They describe lines of effort addressing priority capability gaps that, if implemented, could substantially improve immediate life-saving efforts during WUI fire incidents. The key findings listed below are considered equally important to this objective and are not listed in any priority order.
- Implement and scale the use of state-of-the-art remote sensing assets to provide state and local stakeholders real-time, accurate, low-cost ignition detection and tracking information— especially fire perimeter using a mix of in situ, aerial, and space-based systems.
- Improve the ability of available and adaptable public alert and warning technologies to deliver more targeted and effective message across the whole community, particularly to individuals with disabilities and others with Access and Functional Needs (AFN).
- Improve use of key public and private social media and internet resources and capabilities to appropriately share data and adapt existing applications to enable more efficient and effective evacuation—e.g., expand and accelerate public-private partnerships through Integrated Public Alert and Warnings System (IPAWS) to include WUI incident-related evacuations, warning, and alerting.
- Support broader use of existing fire modeling and forecasting tools for pre-incident planning; while also advancing efforts to create high-confidence, timely WUI fire-specific models that can be used to inform response tactics during extreme conditions.
- Increase infrastructure resilience, especially critical infrastructure lifelines and support functions for wildland fire response—e.g., improve the resilience, interoperability, and reliability of communications, power utilities, digital links, and data center infrastructure.
- Integrate private, open, and crowdsourced data, resources, and capabilities to improve public safety situational awareness of WUI fire ignition detection and tracking.
- Support wide-scale adoption of interoperable, low-cost blue-force tracking technologies that feed near real-time situational awareness across key stakeholders, missions, and operations.
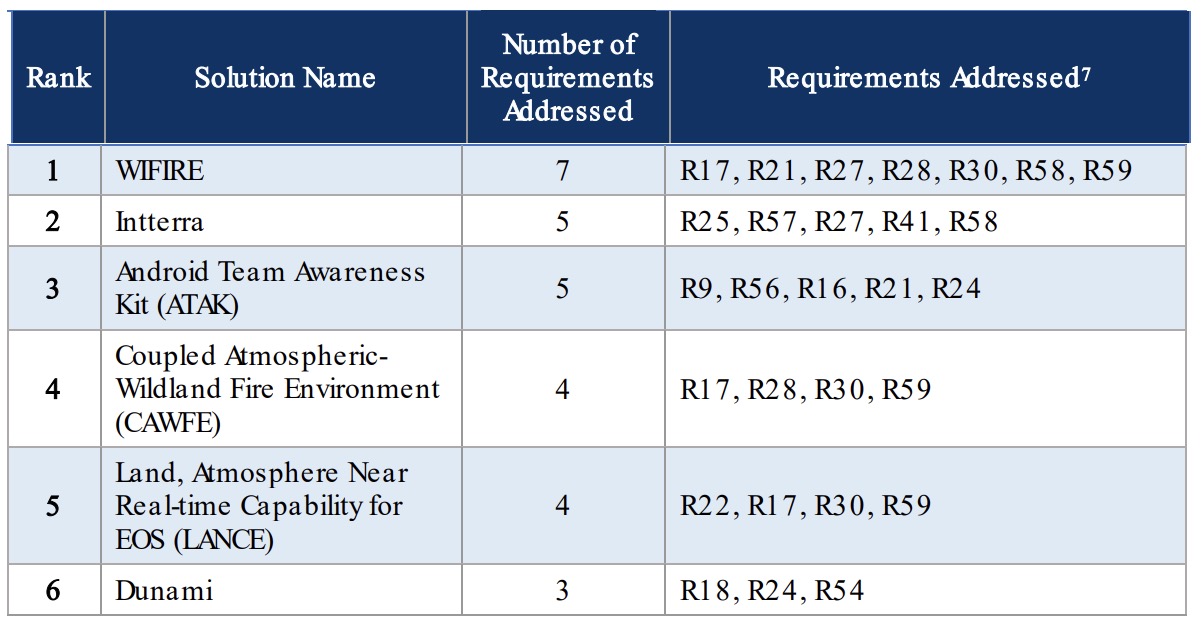
The project team evaluated over 60 existing systems, products, or solutions. Here is an example of how 10 were ranked for how well they addressed requirements.
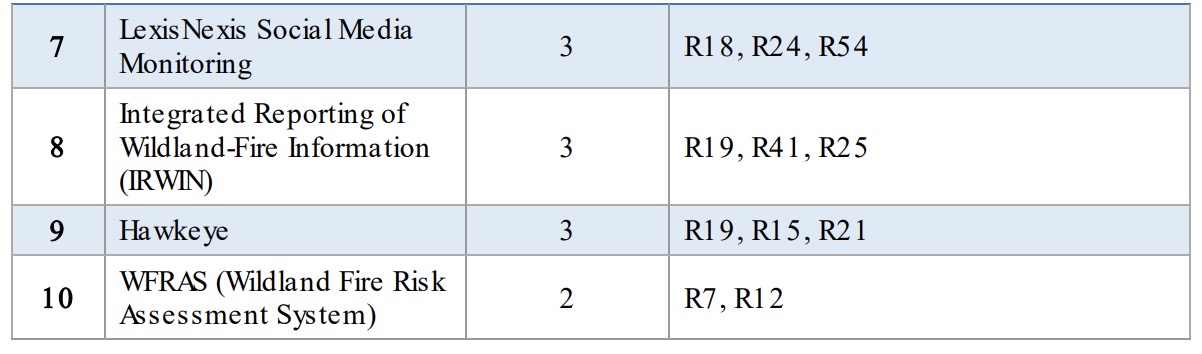
In addition, the team evaluated the solutions for feasibility, affordability, usability, impact, and technology alignment.
The entire 131-page report can be downloaded. 2.8 MB
Thanks and a tip of the hat go out to LM. Typos or errors, report them HERE.

Although well-intended, the report is really incomplete. fiResponse, is in use by Texas, Georgia, Tennesse, Virginia, Mississippi, North Carolina, Florida as their Wildfire Incident Management System, yet has not been reviewed with the level of detail necessary. In addition, Wildfire Analyst is the de facto standard for Advanced Operational Wildfire Modeling in California, including the major Electric Utility companies, regulatory agencies, and the State Authorative Agency. This product was the only one selected by CAL FIRE from 131 submissions to meet their requirements for fire spread prediction. Surely, this level of adoption and advanced capabilities necessitates consideration in this report, beyond the level of cursory research undertaken. These products are also proven worldwide in multiple advanced fire environments, such as Spain, Chile, and Portugal. Also, SimTable is not even mentioned.