Federal firefighters have for years put up with both low pay — starting at just $15 an hour for entry-level positions — and a high-pressure job that takes a heavy toll mentally and keeps them away from their homes and families. Hundreds of them have left federal service, and hundreds more will likely leave next month if a permanent federal pay increase is not approved by Congress.
This fall, as reported by The Guardian, pay issues are coming to a head. A temporary pay increase, effected as part of Biden’s 2021 infrastructure bill, will expire at the end of September. Without that pay increase, the U.S. risks a crisis of firefighter burnout and falling retention while fires increasingly burn larger, hotter, and for longer than they have in decades.

Congress has two weeks to enact a long-term fix. If they fail, federal land management agencies may be left to navigate another mass exodus from the essential workforce just as autumn winds increase risks across the West.
As the Federal News Network recently reported, wildland firefighters are meeting with congressional leaders this week to add urgency to pending legislation that would install a permanent pay raise. The $600 million that funded the two-year pay boost runs out at the end of September.
Back in July, Grassroots Wildland Firefighters launched a petition to tell Congress what’s at stake if they don’t enact a permanent pay solution. In just a week, more than 11,000 wildland firefighters and others signed their names and described what will happen if Congress fails to act. A sample of signers’ responses:
-
- “30-50% of the firefighting force will leave unless signed, including myself. I have bills to pay, I love this job but unless things change, I can’t afford to do it.”
- “I worry that with this pay cut we will lose our hard-working wildland firefighters, and the land that so many of us love and recreate in will be unprotected and destroyed.”
- “One third of the permanent fire employees I know will have to leave the wildland fire profession to pay their mortgage.”
- “As a fire family, this would hit us hard. These men and women who battle fires daily to prevent homes from being burned deserve the most.”
- “Thousands of firefighters walking off the job. Many of us are planning for what happens if they do nothing.”
- “15 years of firefighting and my nephew makes more working at Panda Express. It’s time to recognize our firefighters for what they do and the sacrifice they have put forth to protect public lands.”
“Firefighters don’t want accolades, they don’t need to be called heroes,” says Riva Duncan, a retired USFS fire officer and vice-president of the Grassroots Wildland Firefighters advocacy group. “But they want to at least be treated like they are appreciated for the risks they take and the sacrifices they make.”
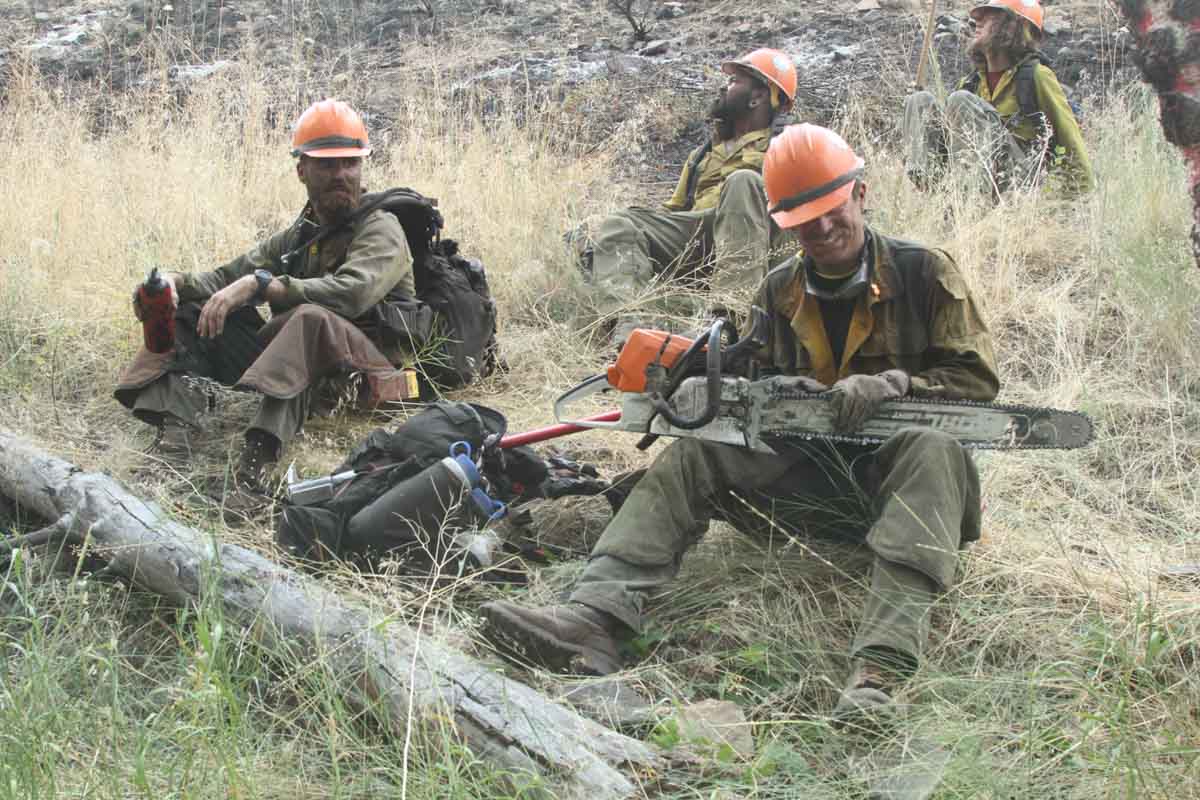

Biden’s temporary pay bump — which added either $20,000 or a 50 percent increase to firefighter paychecks, whichever was less — was intended as a short-term fix to buy Congress time to pass a permanent solution to the problems that have for years left federal firefighters underpaid and overworked.
The National Federation of Federal Employees, the union that represents many wildland firefighters, said without a permanent solution, there will be a “mass exodus” of firefighters, which would only exacerbate retention challenges that are already increasingly difficult for the four Department of the Interior agencies and the Forest Service; all five agencies employ roughly 17,000 wildland firefighters combined.
That story in the Guardian, by Gabrielle Canon, is WELL WORTH the read — and thanks to Nancy for the tip.
Without the passage of new legislation, federal firefighters will see major reductions to their paychecks starting October 1. Some workers’ pay will be cut back to $15 per hour. … California lawmakers, by the way, just passed a bill that would make $20 an hour the minimum pay for fast-food workers in the state. You can sign the Grassroots petition to Congress [HERE].