The California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (CAL FIRE) has released a Green Sheet report about the rollover of a dozer that occurred August 1, 2018 on the Carr Fire west of Redding, California.
Below are excerpts from the 14-page report:
“At approximately 7:00 AM on Tuesday, July 31, 2018, two CWN bulldozers (DOZ1 and DOZ2) were 24 hour resources assigned to Branch III, Division D on the Carr incident. DOZ1’s operator (OP1) had been assigned to the same area on the previous 24-hour operational period (south of HWY 299E on County Line Road) and worked the night shift (7:00 PM to 7:00 AM). OP1 had 4 years of bulldozer operating experience and at least 17 years in the logging industry. OP1 had used the bulldozer extensively in Sonoma and Napa counties in the Fall of 2017.
[…]
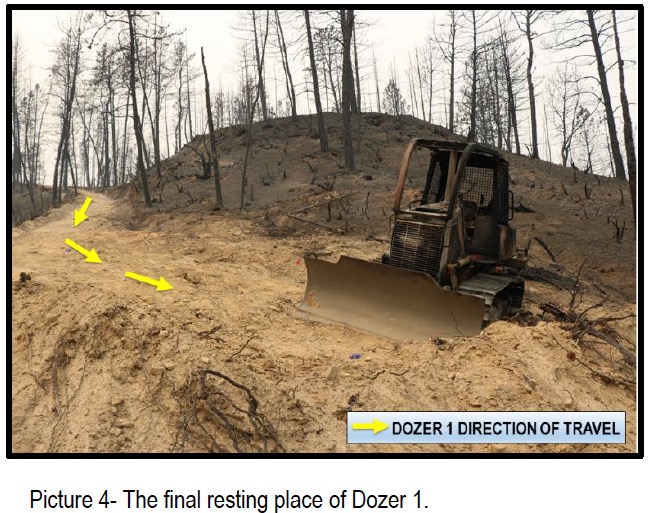
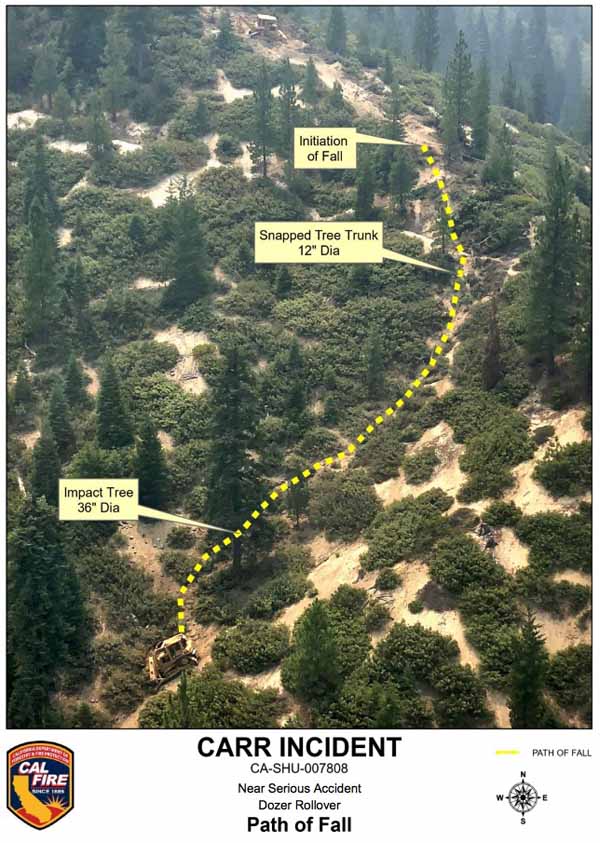
“At approximately 12:30 AM, STL1 looked toward DOZ1, located up the spur ridge and observed DOZ1 close to the steeper east aspect of the spur ridge. From STL1’s vantage point, DOZ1 was facing him and appeared to be tilted to the right at approximately 40-45 degrees. STL1 observed DOZ1 attempt to climb back to the center of the spur ridge in reverse. While DOZ1 backed, STL1 further observed the front of DOZ1 abruptly rotated 90 degrees to the left and the front of the dozer lift into the air. DOZ1 then lost traction and slid backwards downhill, at which time STL1 saw DOZ1 roll twice, end over end, before he lost sight of it down the slope. STL1 could hear DOZ1 continue to roll down the slope, and then stop. STL1 went to the edge of the slope where DOZ1 left the ridgetop, and could see DOZ1 approximately 300 feet downslope.
“At approximately 12:32 AM, STL1 notified Branch II (t) of the accident and his intention to proceed to DOZ1 to ascertain injuries and needs. STL1 contacted DOZ2 to cease operations and then proceeded to DOZ1’s location. Branch II Safety Officer and Division C Fireline Medics responded to the accident site. Carr Communications was notified of the accident at 12:34 AM by Branch II (t).
“While walking downslope to DOZ1, STL1 heard the engine speed fluctuating up and down. STL1 found the dozer upright on its tracks with the cab still intact. STL1 observed movement inside the bulldozer cab. DOZ1 appeared to be stable and STL1 boarded the dozer on the uphill (right) side. The right cab door was jammed and would only open a couple of inches. STL1 contacted OP1 and did a quick visual assessment. OP1 suffered injuries to the head but was alert and oriented.
“At approximately 12:35 AM, STL1 updated Branch II (t) of OP1’s condition via radio. Branch II (t) advised STL1 to follow the “Incident Within an Incident” protocol in the Incident Action Plan. OP1 self-extricated through the left cab door. With OP1 sitting on the ground, STL1 performed a thorough secondary patient assessment. A night hoist capable helicopter was requested due to mechanism of injury, patient location, and extended ground transport time to a medical facility. A California National Guard night vision equipped 24-hour helicopter medivac resource, assigned to the incident, responded from Redding Helibase and an Advanced Life Support ground ambulance was dispatched to Hwy 299E and County Line Road (Buckhorn Summit) from their staging area in west Redding.
“Division C Fireline Medics arrived at the accident site at 1:35 AM. Due to a heavy smoke inversion, the helicopter experienced difficulty accessing the accident site and at 2:01 AM, Division C Medics cancelled the helicopter and walked OP1 out to meet the ground ambulance. OP1 was transferred to the ALS ambulance at 2:43 AM and began transport to Mercy Medical Center with a 2-hour estimated time of arrival…”