After the 2019-2020 southern hemisphere bushfire season, emergency management personnel in both the United States and Australia should take the opportunity to evaluate the fire season and determine if there is a better way of distributing information to the public and emergency management agencies. In neither country is there one key source for information where the public, the media, and the responsible agencies can quickly and efficiently obtain important real-time intelligence and predictive models that they need to make decisions about informing the public, mitigating the emergencies, providing relief, managing transportation corridors, and gathering information about electrical power grids and evacuations.
The military calls this information source a common operating picture (COP).
All of this information is available at hundreds if not thousands of sources, but not everyone that could benefit from the data have access. It needs to be pulled together for safety and efficiency.
In the United States if a citizen needs current information about a wildfire how do they get it? From the county sheriff, local fire department, or a county, state, or federal agency? It makes a difference about where to look if the fire is on federal land, state protected land, city, county, national or state park. They can try social media, but which application and which account? InciWeb sometimes has information about wildfires managed by federal agencies, but not all. And since law enforcement is responsible for evacuation, InciWeb does not always have current information about the status of evacuations. Information on the website about individual fires may not have been updated for 12 to 18 hours, however some incident management teams are better than others. And InciWeb rarely provides projections of fire spread in a timely manner, if at all. When someone is threatened by a rapidly spreading wildfire they don’t have time to randomly check an alphabet soup of acronyms on dozens of web sites or social media accounts, even if they know the names, handles, or web addresses.
A COP would need to have a sign-in option that would make it possible for authorized personnel to see detailed data that should not be distributed to the whole world, such as exact locations of resources.
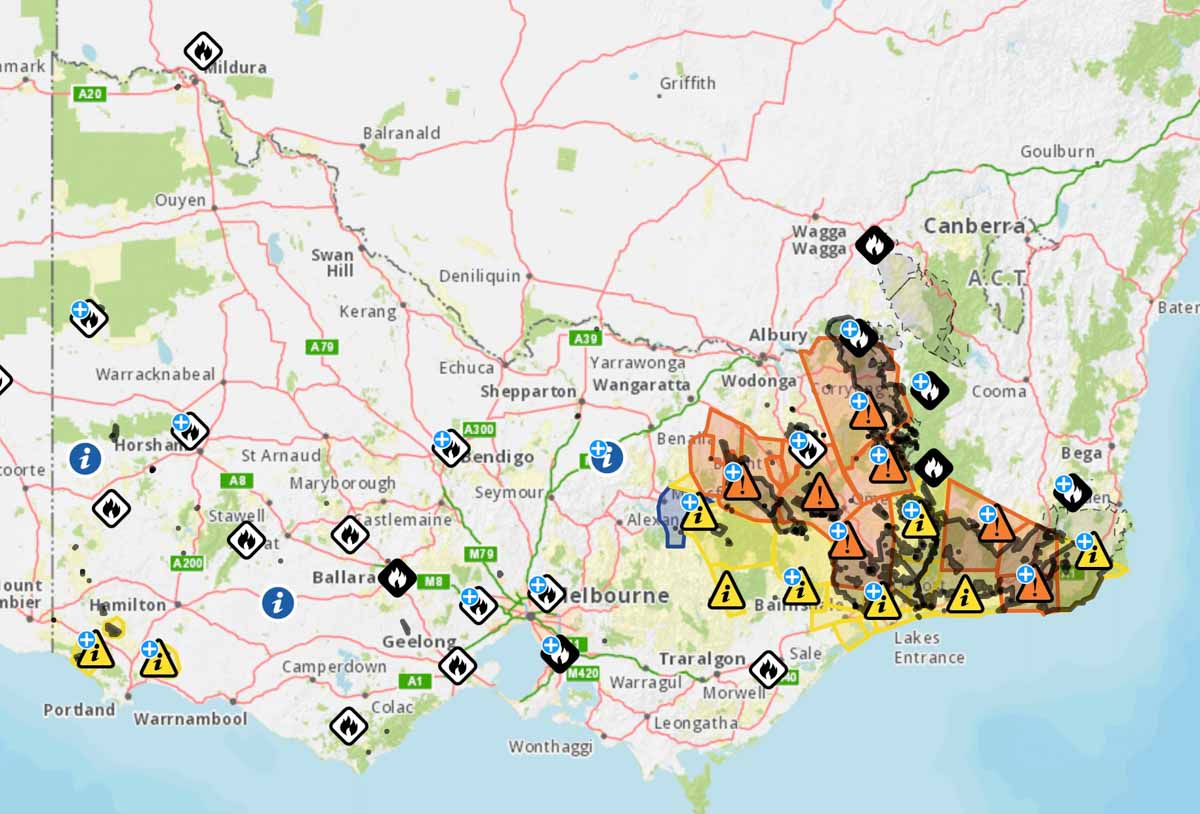
Below are examples of fire location information in Australia on January 6, 2020 United States time, in addition to the Victoria map at the top of the page.
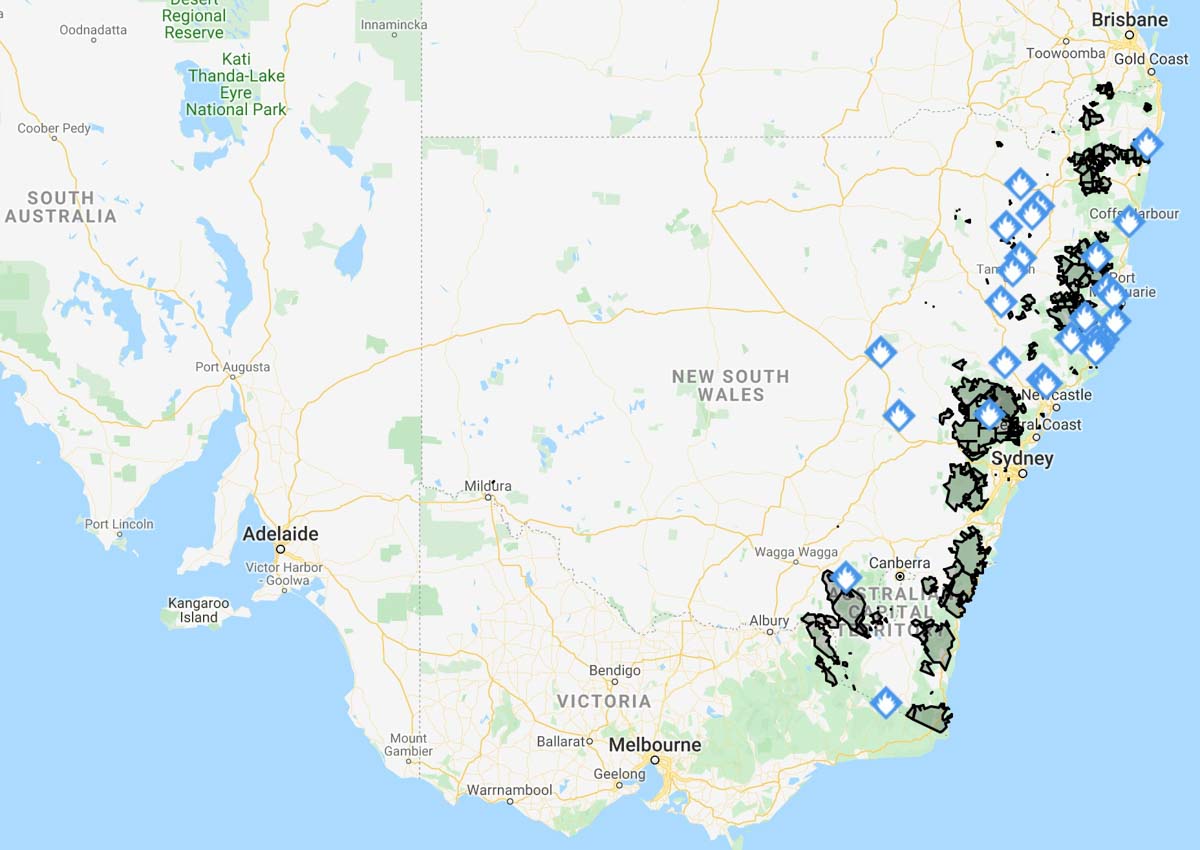
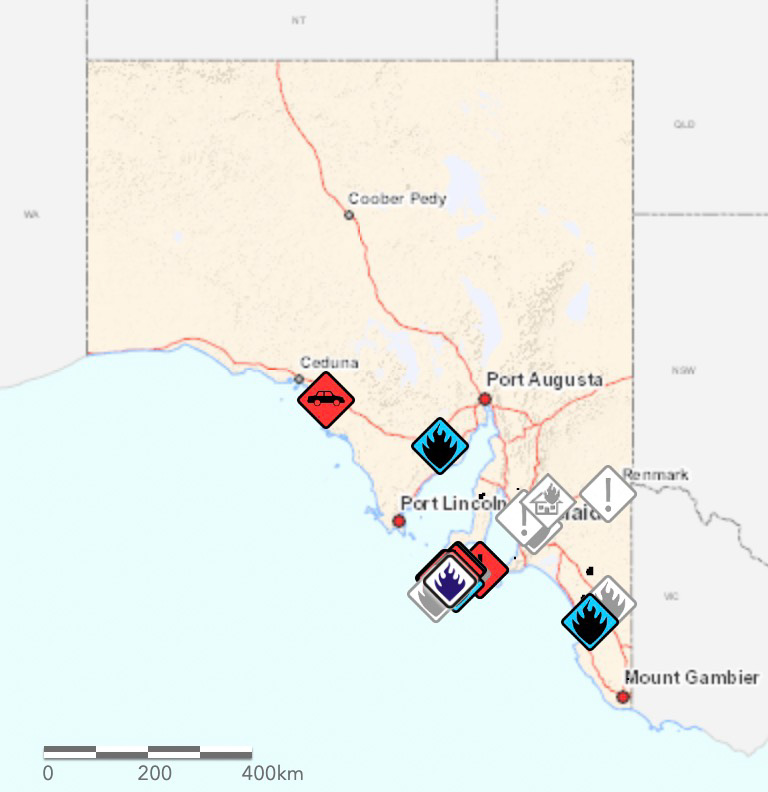
The maps produced for New South Wales and South Australia can be more useful upon zooming in, but occasionally they are so cluttered with multiple polygons and symbols that they are difficult to decipher. The Victoria map improves after zooming in, but it tries to include too much information.
The data on these three maps stops at the imaginary line separating the states. This could give someone the false impression that there are no fires just across the state border. If you need information about a location near a state line you need to know how to access the data for both states.
The three Australian states all use different symbology, so an icon or polygon on one map may have a completely different meaning in the neighboring state.
The New South Wales Rural Fire Service occasionally produces detailed maps showing the perimeter of a single fire and the predicted spread, but it is not done on a regular basis and may be difficult to find when it does exist.
But these Australian state maps attempt to include at least some information about all large bushfires in their state. In the United States no agency to my knowledge even attempts this. InciWeb produces a map of the country that shows the location of every fire on federally managed land that is being tracked on the website, but does not include federal fires that are not on the site, or state or locally managed fires.
For both Australia and the U.S. creating a national map for wildfire information would be a great first step toward a common operating picture.
Check out Ellen Broad’s thread on this mapping topic. She has some excellent observations.
This should be a priority…. https://t.co/IXvmL6LTHu
— Wildfire Today ? (@wildfiretoday) January 4, 2020

Creating a COP generally requires a common commander with a common command and control system and standardized/ common C2 infrastructure.
Today’s internet, cell phones, tablets, and laptops afford a common infrastructure. What is lacking is a common command and a common command and control system.
Ask the question: Who is in charge of firefighting? If there is a single commander, building a COP is possible. Otherwise the problem becomes one of creating a COP for a confederacy of organizations and governments all responsible to some degree for commanding firefighting.