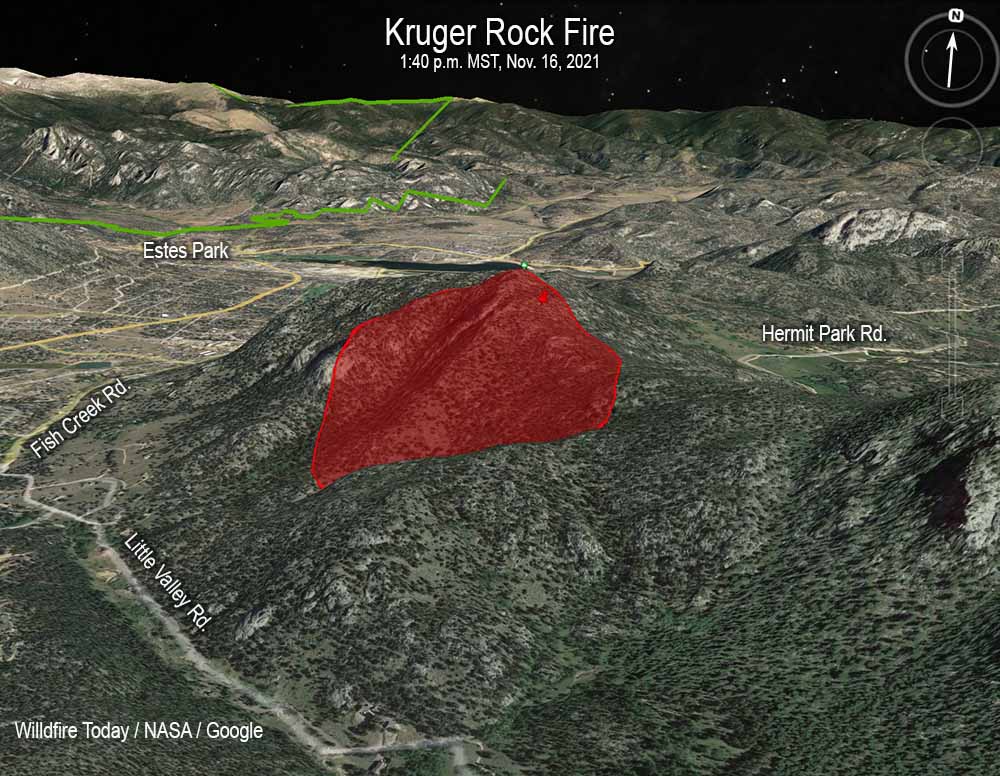
1:59 p.m. MST Nov. 18, 2021
This article was first published at Fire Aviation.
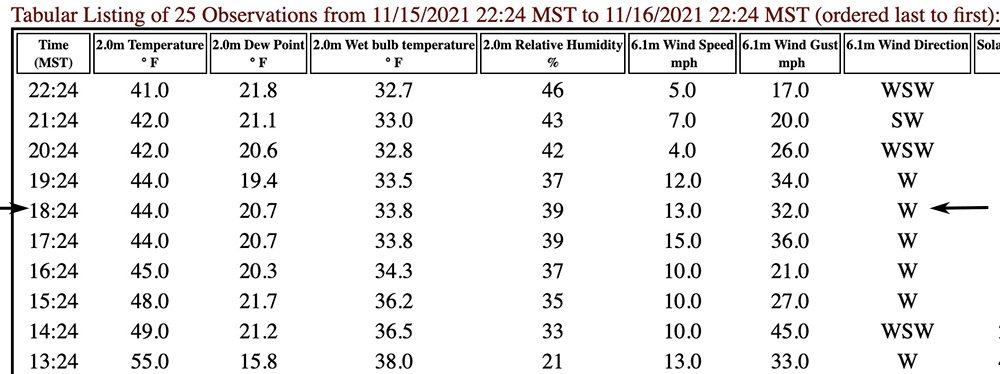
Around the time Single Engine Air Tanker 860 crashed at the Kruger Rock Fire in Colorado at approximately 6:36 p.m. MST on November 16, killing pilot Marc Thor Olson, the Estes Park ESPC2 Remote Automatic Weather Station recorded sustained winds of 13 mph gusting to 32 mph out of the west. The station is 3.7 miles northwest of the fire at 7,892 feet and its anemometer is 20 feet above the ground.
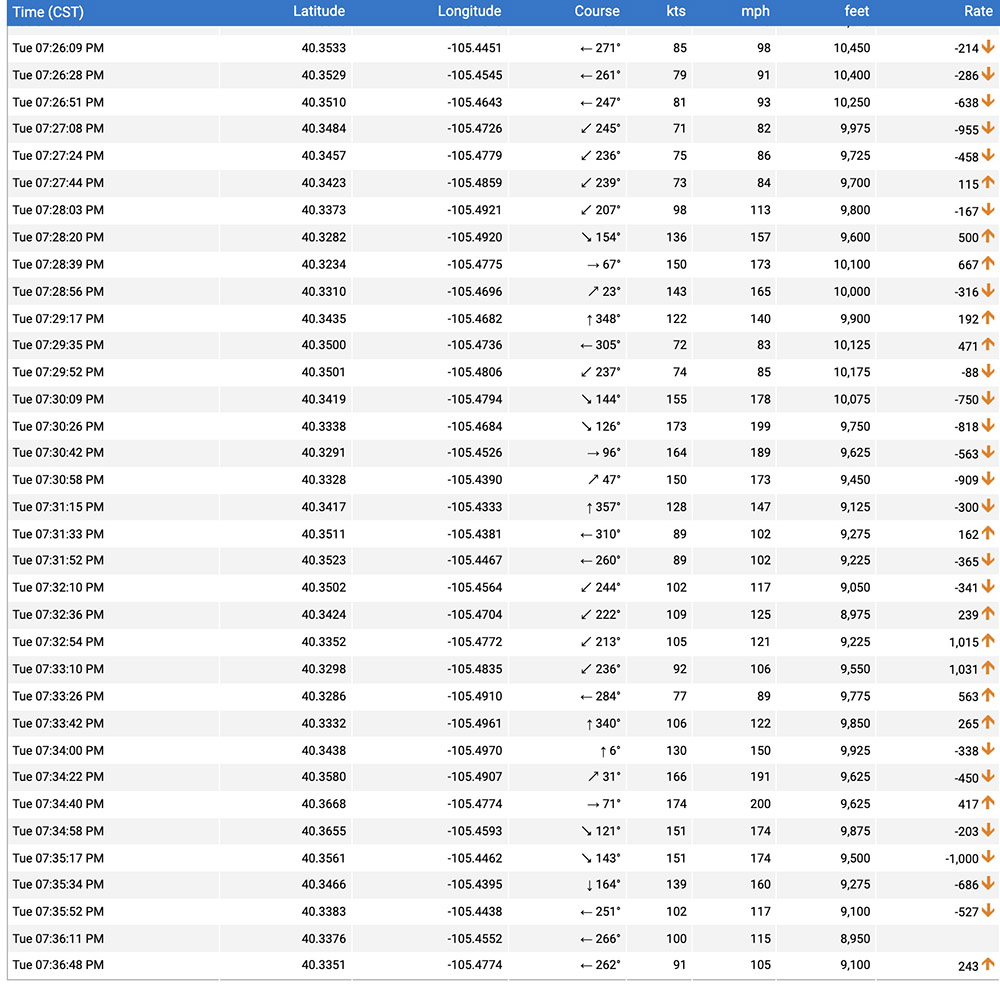
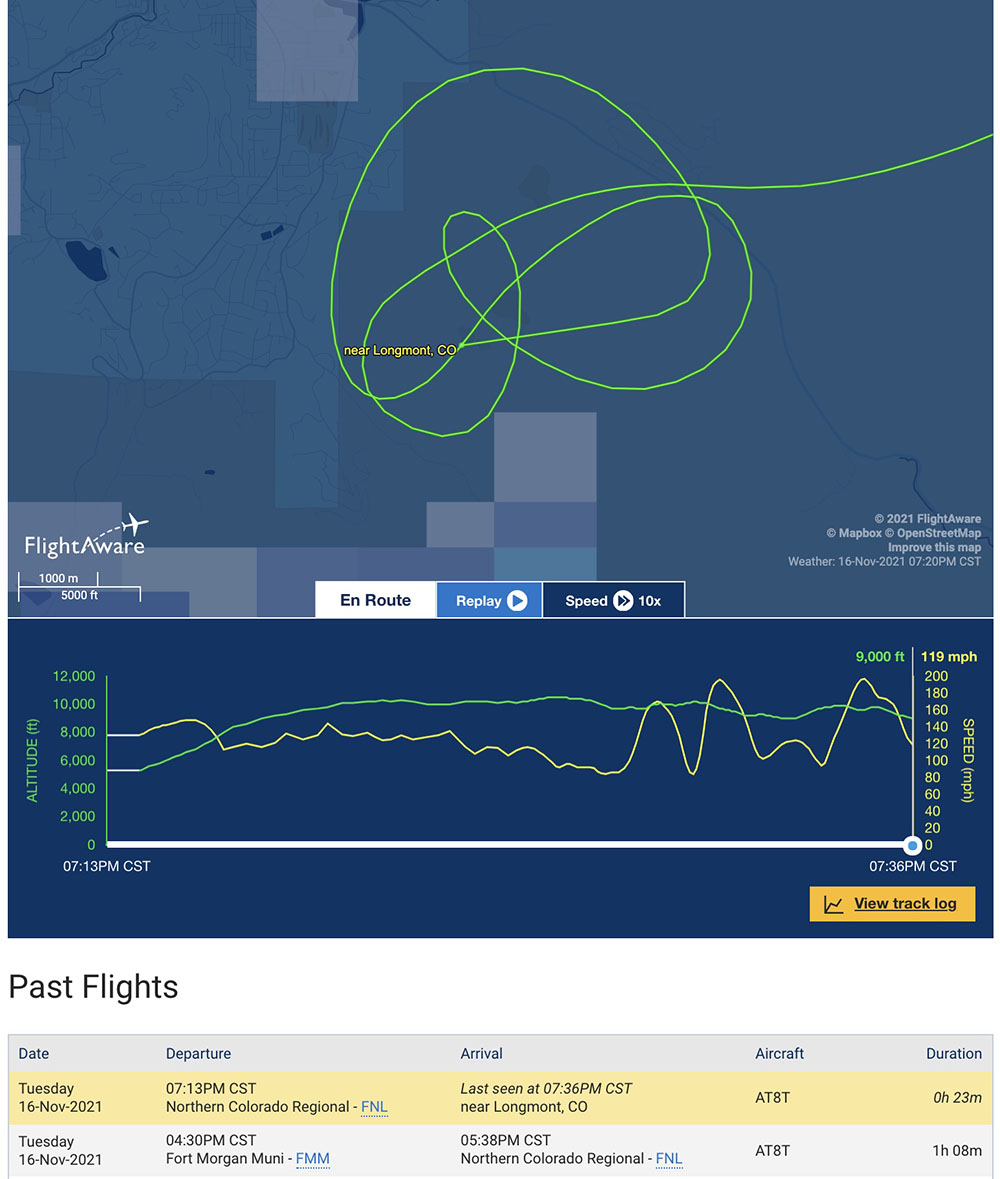
Looking at the flight tracking log from FlightAware above, the wind appeared to be much stronger at the plane’s altitude, which was 8,950 to 10,450 feet while it was over the fire. The highest peak just south of the fire is at 9,400 feet.

As it made four orbits near the fire during the 10 minutes it was in the area, the ground speed of T-860, an Air Tractor 802A (N802NZ) varied from a low of 82 mph while flying west to a maximum of 200 mph when east-bound. These shifts in ground speed were consistent during all four orbits. This indicates a very strong wind out of the west, a direction that is consistent with the data from the weather station.
There are two reasons that fixed wing air tankers avoid attacking wildfires during strong winds. One, the wind makes it difficult or impossible for the retardant to hit the target, getting blown horizontally as it falls from the aircraft to the ground. Second, flying low and slow, as air tankers have to do, is difficult in mountainous terrain with calm winds, but it can be extremely hazardous during strong winds.
When you add a third complexity of dropping at night using night vision goggles, something that has been done very little in the history of aviation, and never before in Colorado, the pilot had the deck stacked against him. The chances of stopping or slowing the spread of the fire with retardant, water, or any other suppresant, were very, very slim. (There is a report that the operator of the aircraft, CO Fire Aviation, experimented with night drops in Oregon in 2020 and 2021.)
NEW: CO Fire Aviation confirms the pilot killed in the air tanker crash last night was Marc Thor Olson. He told me most people called him Thor.
This is a picture I took of him last night as he was prepping his plane. The crash happened about an hour later #9News pic.twitter.com/uEOO4tbXwK
— Marc Sallinger (@MarcSallinger) November 17, 2021
The weather forecast available from the National Weather Service that Tuesday afternoon called for continued very strong winds until sundown and a chance for snow Tuesday night. It predicted dry weather on Wednesday and Thursday with high temperatures in the 30s and 40s under mostly sunny skies with the relative humidity around 20 percent. The wind chill was expected to be below zero from Wednesday afternoon until Thursday afternoon. The actual low temperature Tuesday night turned out to be 11 degrees.
Risk vs. reward
With 20/20 hindsight looking at risk vs. reward, this was a very high risk mission. The potential reward was little, considering the likely effectiveness of 700 gallons of suppressant blown off target by strong winds and the weather forecast of a chance of snow in a matter of hours and wind chills the next day below zero.
Who decided to attempt the night flight?
The short answer is, the Larimer County Sheriff’s office ordered the aircraft to respond to the fire, using a “verbal call when needed contract”, an arrangement that was first agreed to on October 5, 2021.
A preliminary map appears to show that the fire was just inside the boundary of the Roosevelt National Forest. The Larimer County Sheriff’s office said on Wednesday Nov. 17 that as of 7 a.m. that day the fire was being managed by a unified command with the US Forest Service and the Sheriff.
In Colorado, Texas, and Wyoming the local county sheriffs are given the responsibility for suppressing wildfires outside of cities unless they are on federal land. The Kruger Rock Fire was in Larimer County.
As Wildfire Today reported November 16, before the fatal flight, T-860 departed from the Fort Morgan, Colorado airport, orbited the fire about half a dozen times, then landed at Northern Colorado Regional Airport at 4:38 p.m. MST. This flight is listed in the image from FlightAware above as one of two flights that day for the aircraft. It turns out that on the first flight it dropped water on the fire, which the pilot reportedly described as “successful”. After it landed at Northern Colorado Regional Airport it reloaded with “fire suppressant” instead of water, and by 6:13 p.m. MST was airborne returning to the fire.
Sunset that day was at 4:44 p.m. MST. The air tanker disappeared from tracking at 6:35 p.m., about 1 hour and 49 minutes after sunset. Air tankers working for the U.S. federal government are allowed to drop only as late as 30 minutes after official sunset.
The Denver Post reported that CO Fire Aviation said in a statement, “There was no aerial supervision or lead plane required for the mission and weather and wind conditions were reported to be within limits of our company standard operating procedures.”
In the video below Juan Browne has strong feelings about this incident. Shortly after posting it, he wrote a comment saying, “GROUNDSPEED NOT AIRSPEED!”
Below is an excerpt from a statement released November 17, 2021 by the Larimer County Sheriff’s office:
Continue reading “A weather station recorded strong winds as air tanker crashed on Kruger Rock Fire”