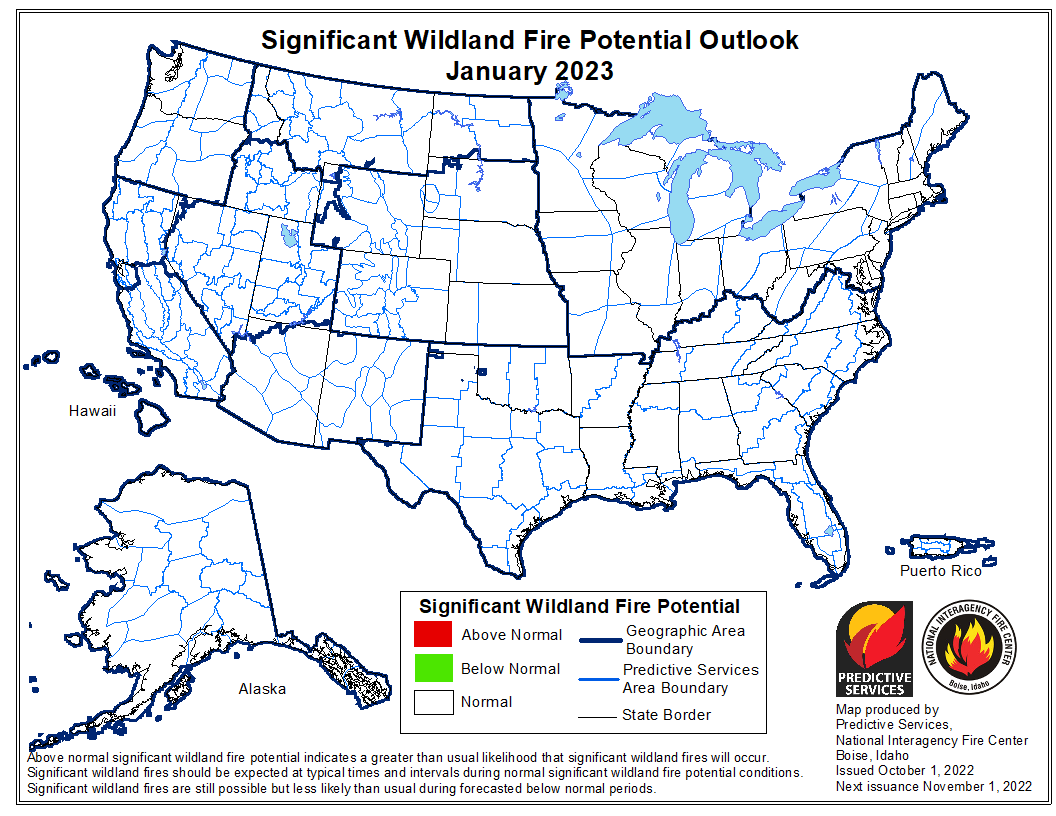
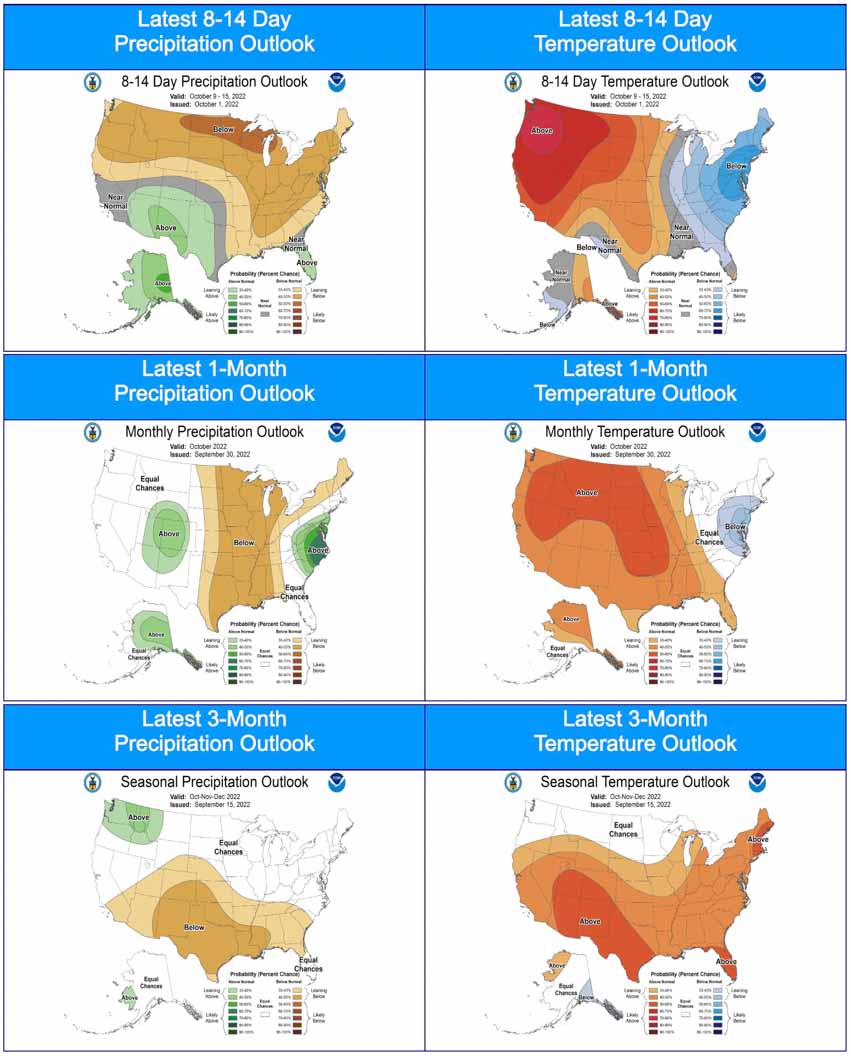
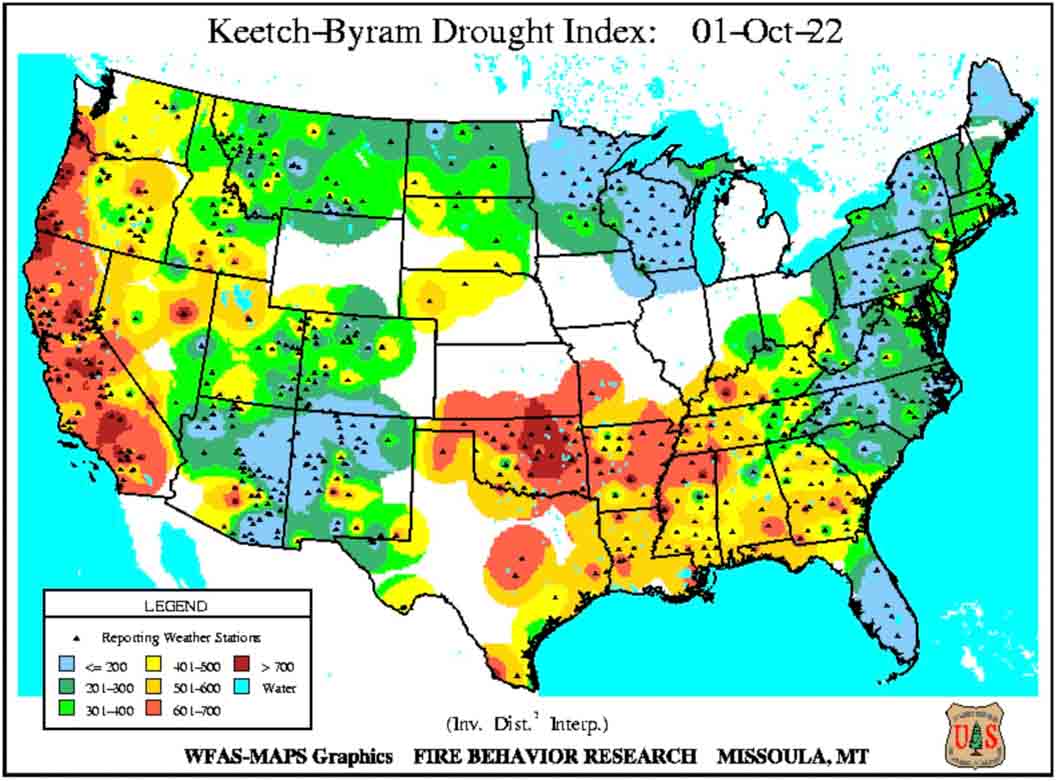
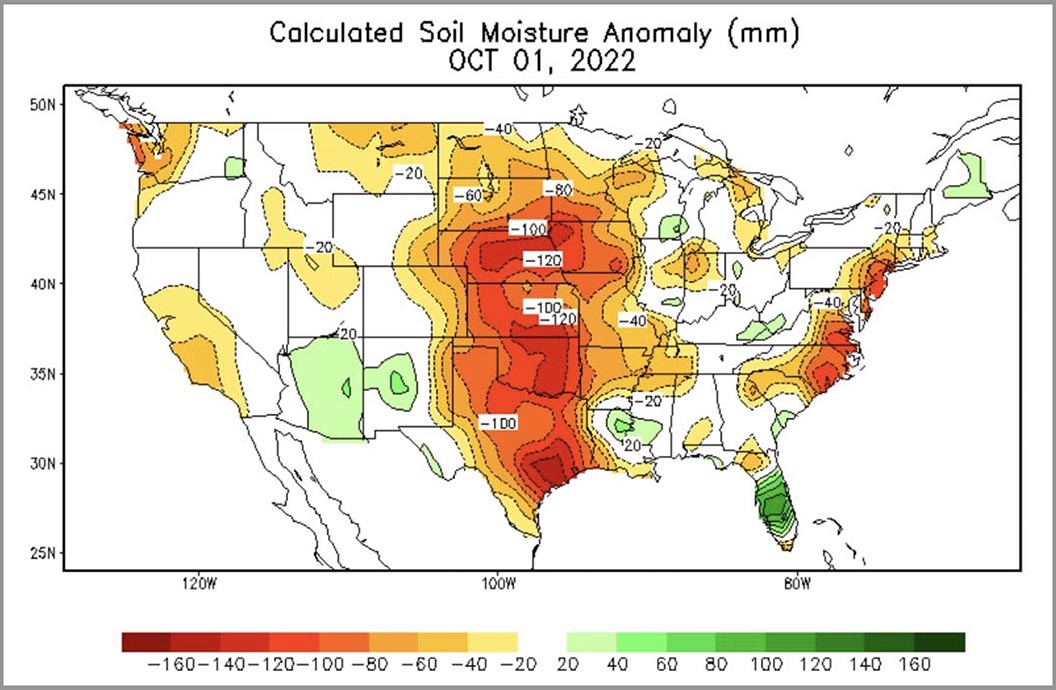
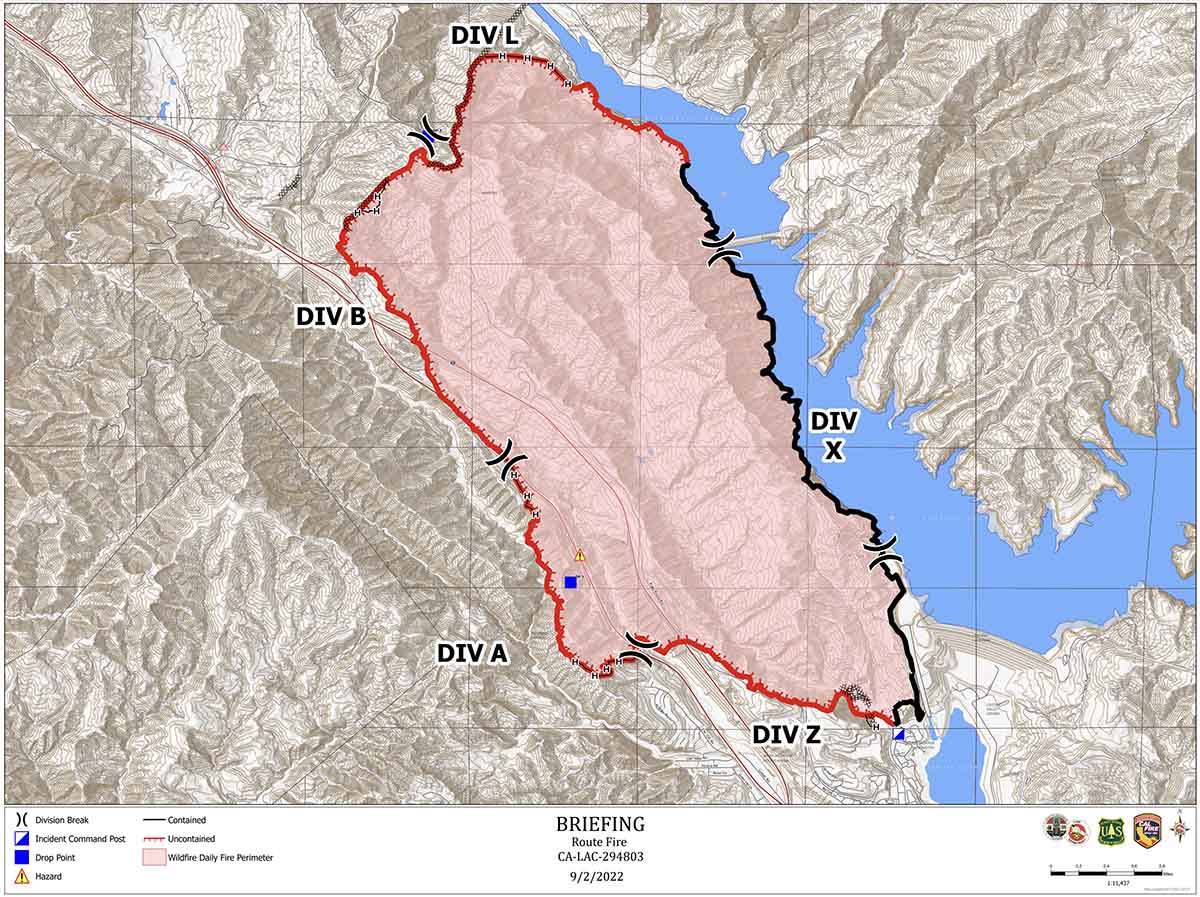
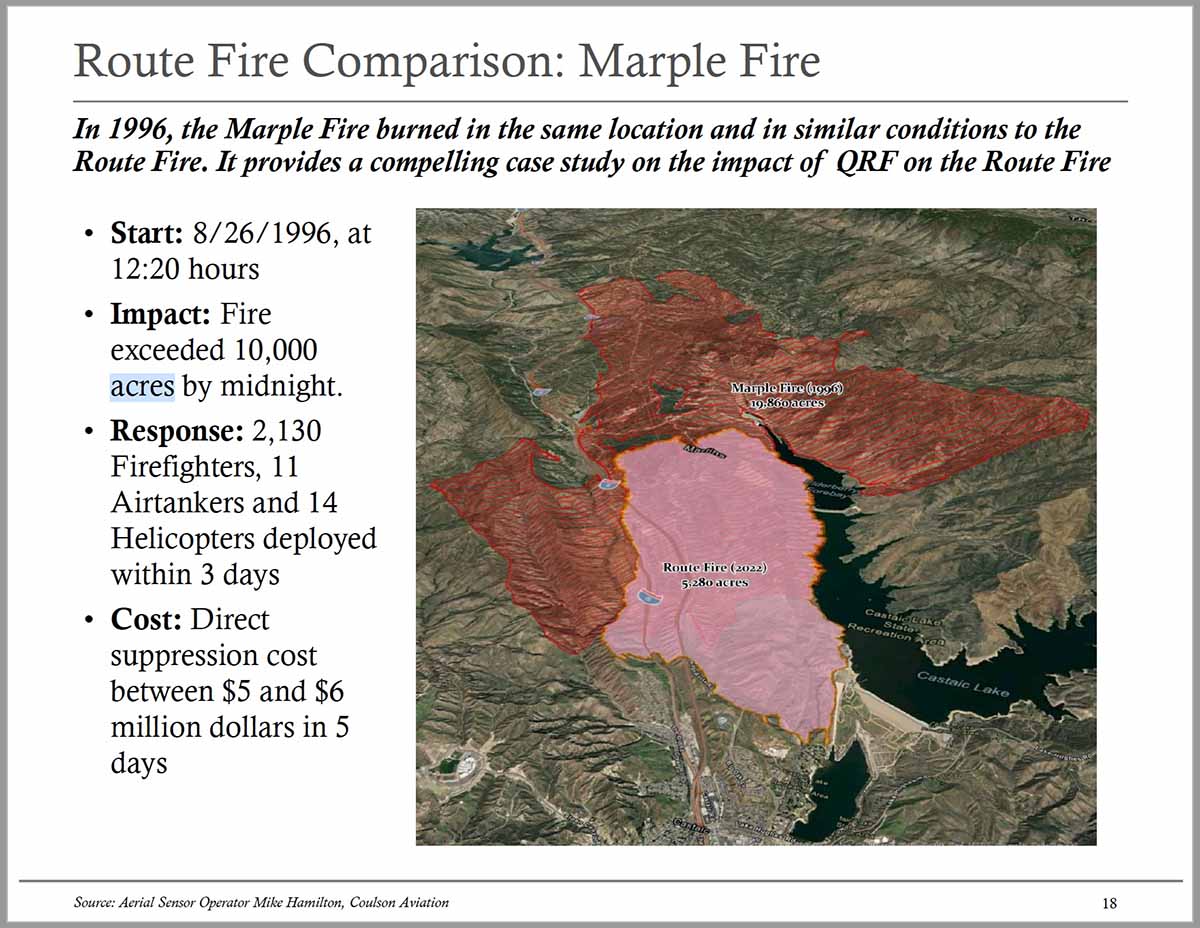
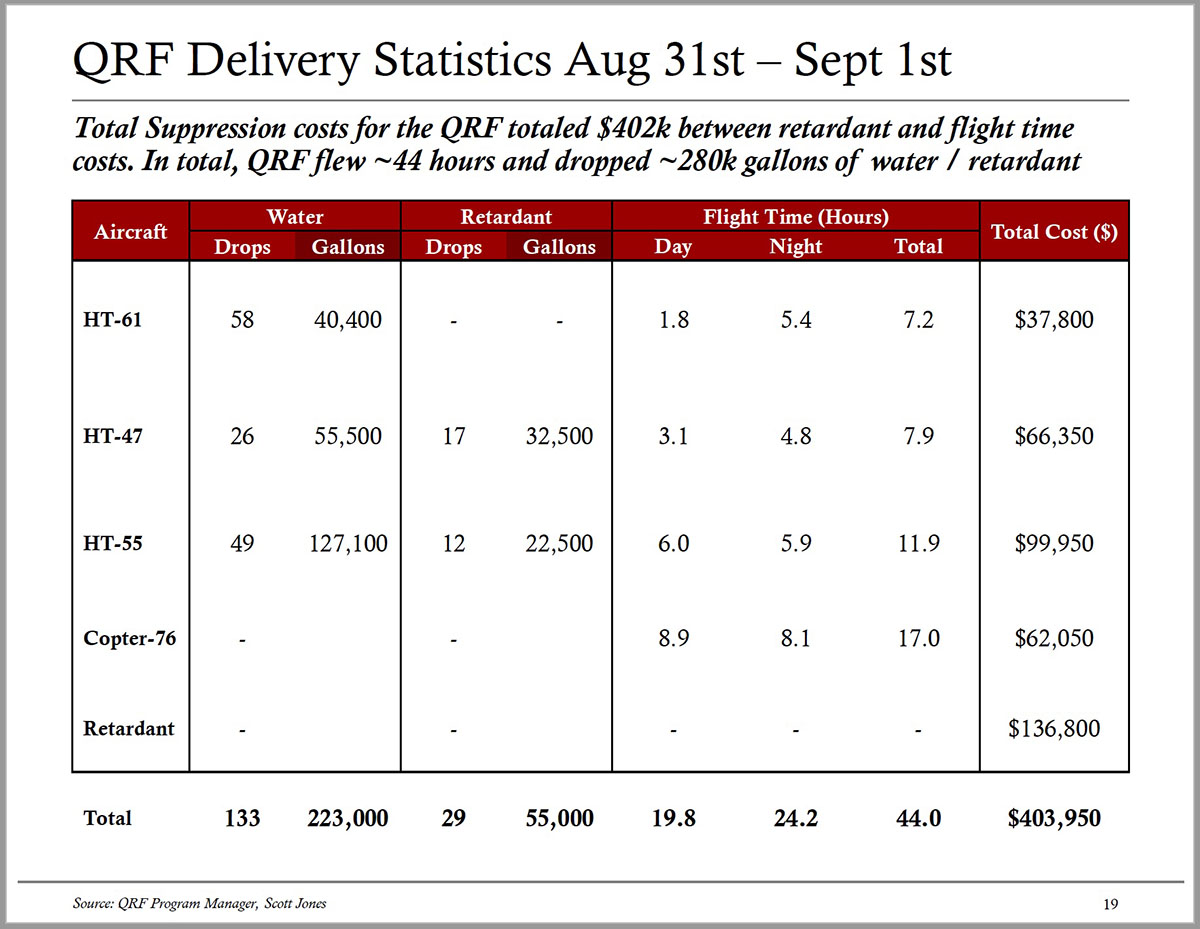
Today President Biden made remarks at the Summit on Fire Prevention and Control addressing the nation’s fire service leaders, commemorating Fire Prevention Week, honoring the bravery and heroism of our nation’s Firefighters, and discussing efforts to protect our communities and ensure Firefighter health and safety amidst the ongoing climate crisis. The summit happened during Fire Prevention Week, which began on Sunday. It is the 100th year of the week’s observance.
You can read the full text of his speech and see the video. Below are excerpts.
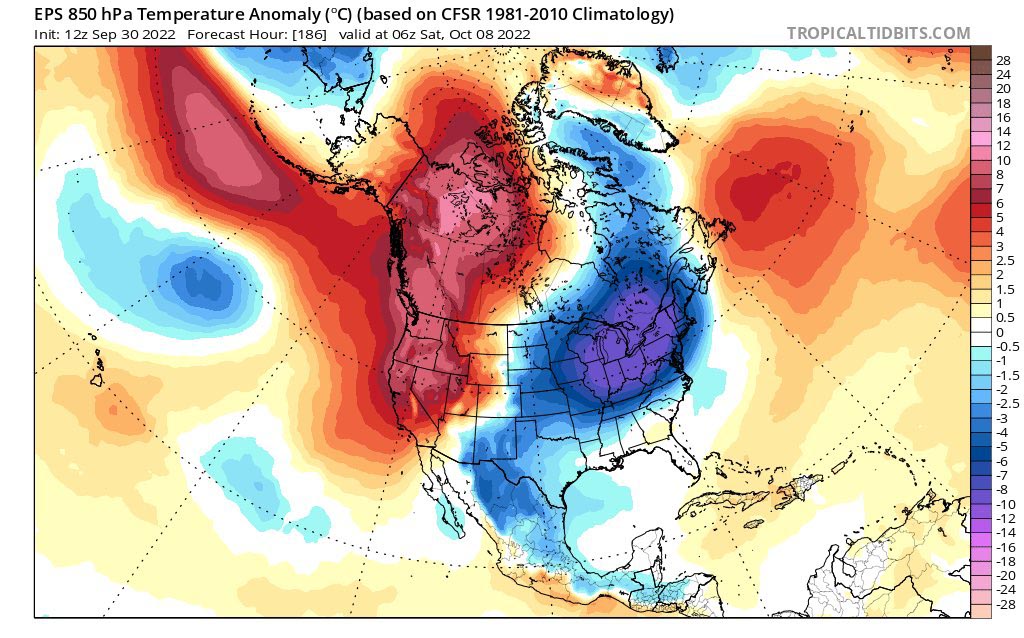
…And when the impacts of climate change are becoming increasingly evident, we’re calling on you more and more and more.
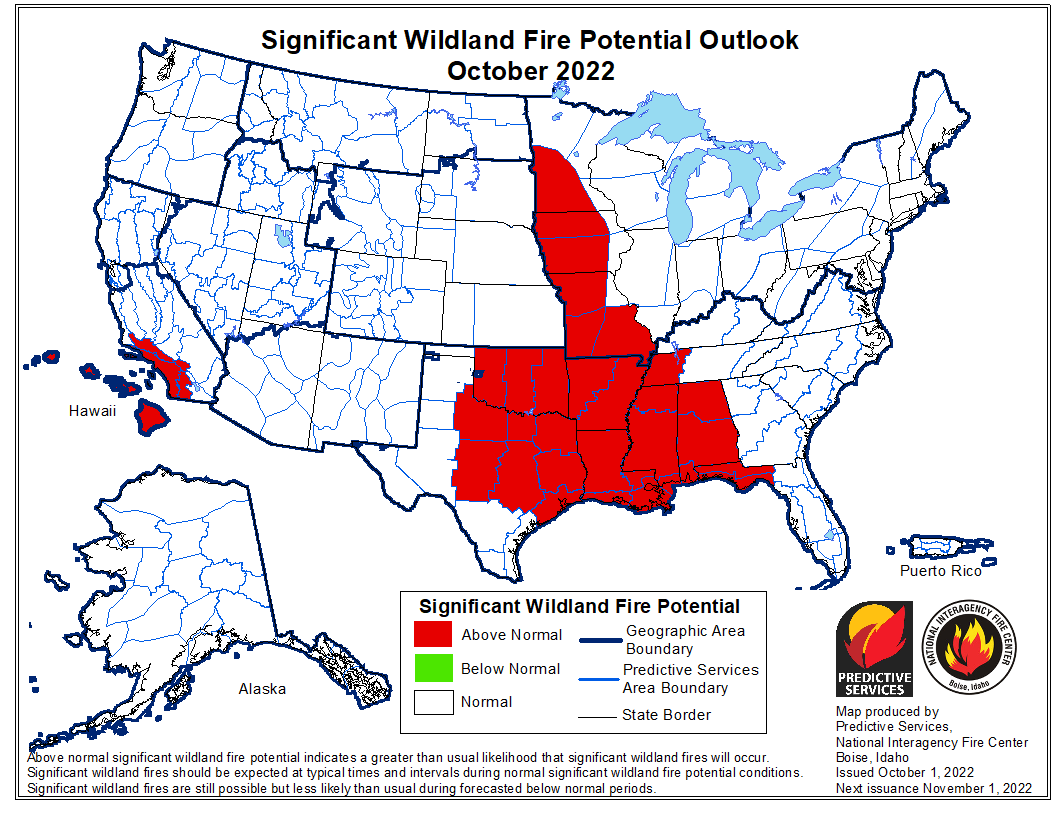
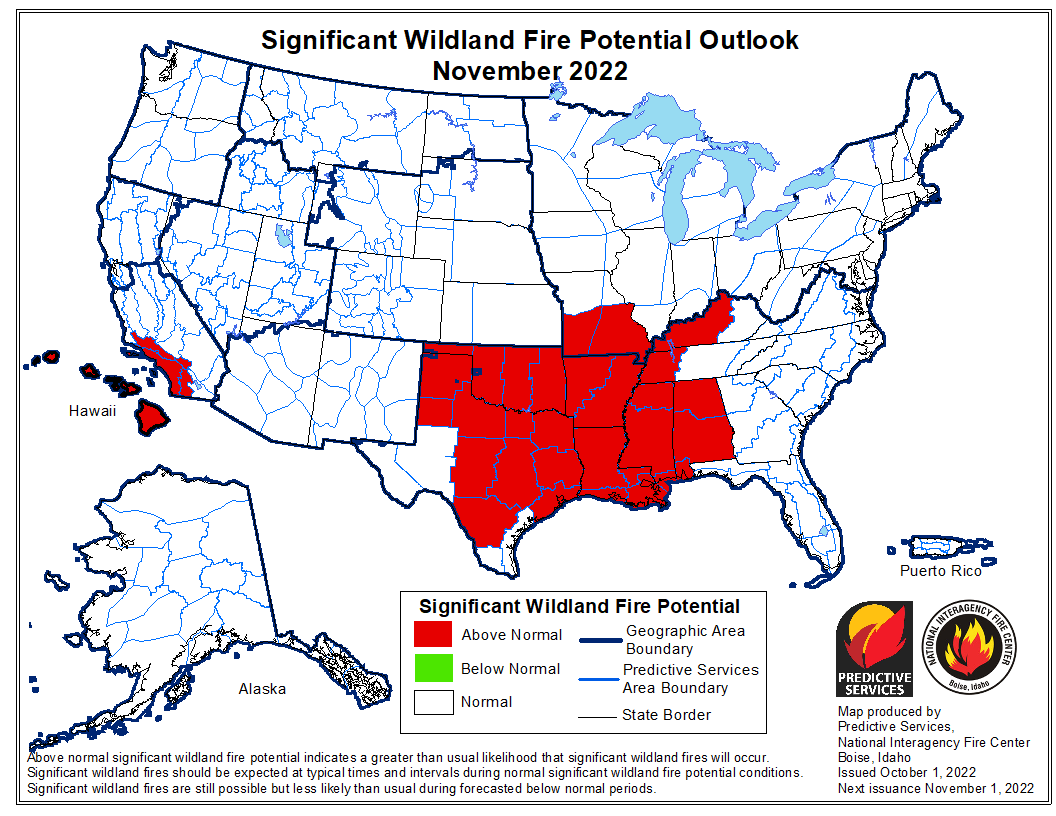
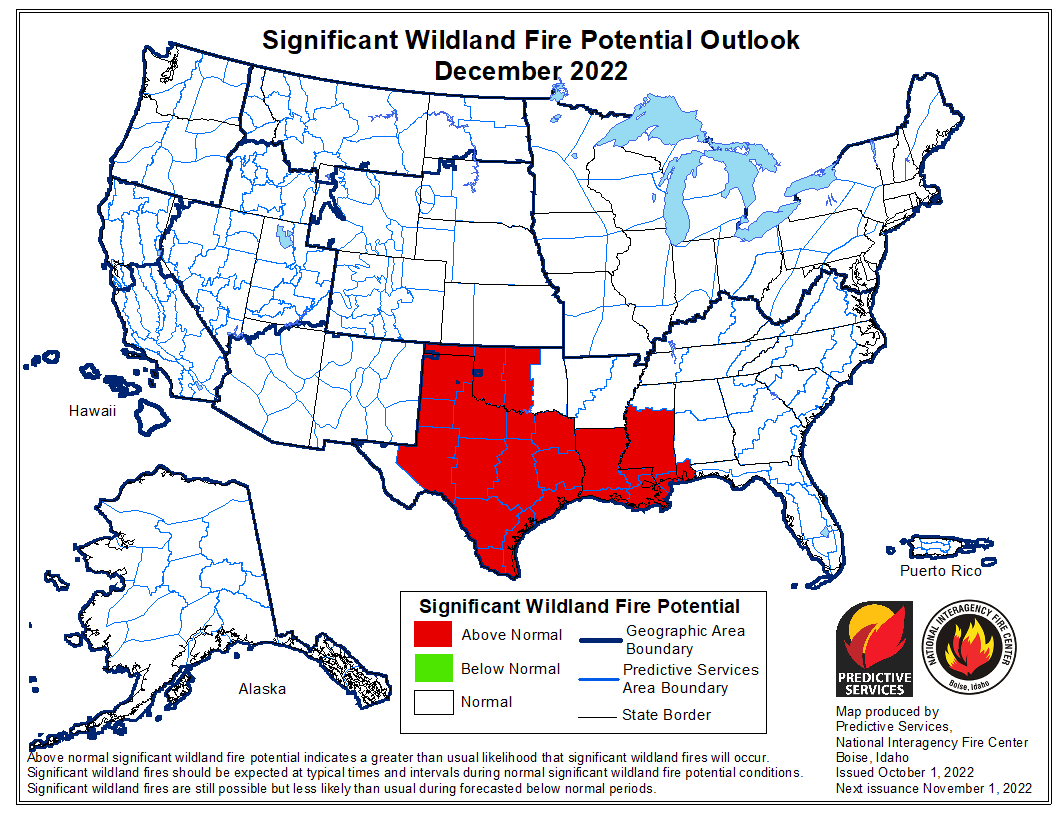
Extreme heat and prolonged drought have turned wildfire season into wildfire years. And local firefighters are being called in more to respond to the fires in the wildland urban interface where we’re moving out into the forest areas to develop and it becomes local and federal.
So I want you to know that my administration is doing everything we can to make sure you have the resources you need to do your job as safely and effectively and efficiently as possible.
You know, we invested $350 billion in the American Rescue Plan to help states and local — states and cities keep first responders on the job, including firefighters on the job when — during COVID-19.
And between the American Rescue Plan and my 2023 budget request, we’ve increased federal firefighting grants by $320 million, which includes money to fund 1,200 more local firefighters in the field, hundreds more emergency response vehicles, and thousands — thousands of sets of turnout gear. A pioneer in research on issues from — including like cancer prevention.
You know, it’s close to my heart. Cancer is a leading killer of firefighters. Toxic substances you’ve been exposed to as part of your job are almost certainly — certainly connected to those cancer diagnoses. And we’re doing — we’re going to do something about it.
We created a special claims unit at the Department of Labor to ensure that they’re processing federal firefighters’ cancer claims quickly.
And I’m urging Congress to send to my desk the Federal Firefighters Fairness Act — let me say it again: the Federal Firefighters Fairness Act — which are going to help federal firefighters and their families assess critical worker compensation resources, including making sure that several forms of cancer are presumed to be caused — presumed to be caused by the firefighter’s job. [Note from Bill: the legislation passed overwhelmingly in the House, but it is bogged down in the Senate.]
And I’m also — I’m also proud that last November, I signed into law Protecting America’s First Responders Act, which extends the benefits under the Public Safety Officers’ Death Benefits Program to the families of firefighters killed in training and made it easier to qualify for permanent disability.
The final point — I’m sorry to go on so long, but I feel passionately about this. The final point I’d like to make today is that we’re doing everything we can to ease the burden on our firefighters by preventing fires. This is the 100th — hard to believe — it’s the 100th anniversary of Fire Prevention Week. And the landmark legislation I’ve signed into law includes historic investments to reduce the risk of fire.
The Bipar- — the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law includes significant forest management, increases community resilience and — to wildfires, and harnesses new technologies to keep communities safe. It’s also repairing vital infrastructure and — firefighters and other first responders rely on to quickly get to the — to those — those in need.
You know, the Inflation Reduction Act enables us to take unprecedented steps to confront climate crisis, which is going to protect forest health, reduce fire risk, and supercharge our clean energy future.
We’re also maximizing protections for people when fires do break out, through a national initiative to help states, local, and Tribal and territorial governments adapt and adopt the most up-to-date building codes that reflect the threats from the climate — from climate change.
Look, on behalf of my own family and every American, I just want to close by saying again: Thank you, thank you, thank you. Fires will always be a fact of human life. And when the worst happens, when those alarms go off, when everything and everybody you love is in danger, there’s no better sight in the world than that firefighter who’s ready to go to work.
So, thank you for being who you are. Thank you for all the heroes you represent. You are — you are on the alert and on call in communities all across this country right now as I speak.
So God bless you all. And may God protect our firefighters. Thank you for letting me have a chance to talk to you. I wish our — I literally do wish I were there with you. Thank you. And thank you, Lori.