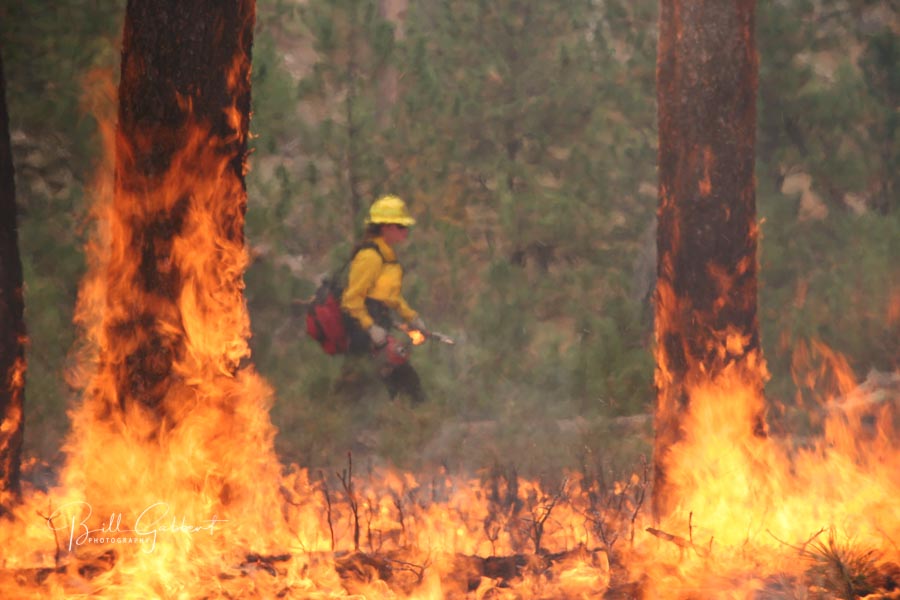
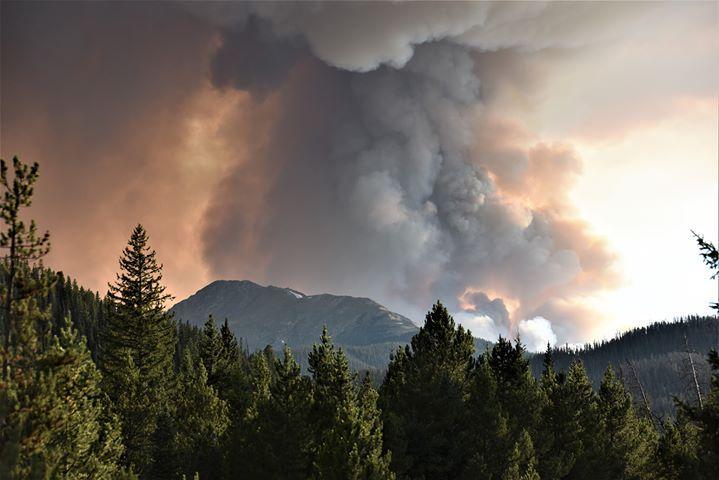
By Anonymous
Note: For the purposes of this article and ease of language I will be referring to “forestry technicians” (our official job title) as “wildland firefighters.” I and many of my cohort strongly identify with the latter classification.
I am a federal wildland firefighter experiencing mental health issues. It doesn’t matter who I am, where I work, or what my demographics are because there are many like me. In the middle of my career, neither fresh nor wise, I am facing some tough questions. By explaining my perspective I hope to shed light on this worsening epidemic. Maybe my experience will encourage people to check in on their employees, peers, family or friends in fire. Perhaps with the countless other stories coming out these days policy-makers will listen and start to adjust their tactics.
There have been bad fire seasons before; I’ve worked too many hours with unpleasant people, had tyrant bosses, and experienced a smattering of sexual harassment. There was Yarnell. I’ve weathered it all not with grace but with sheer tenacity. Of course I’ve made my share of mistakes, talked back when I should have kept my mouth shut, kept my mouth shut when I should have spoken up, but I consider myself an average federal employee in this regard. I’m good at my job and maintain a high level of passion for it.
In all honesty I’ve struggled with mental health in some form most of my life. I do not believe this invalidates my experience or the responsibility of the agency to recognize its problems. Certainly the all-or-nothing seasonal nature and high levels of true stress don’t help and even augment mental health issues. Lack of commensurate pay and benefits take their toll on morale as well. A global pandemic, amplified racial tensions, and drastic climate change contribute to the daily anxiety of most people whether they are in fire or not. Our issues are not unique but they are perhaps amplified, and with more potential for danger. In any case here I am now, taking leave from a job I mostly love and mostly need to get by.
I’m convinced my first season on a hotshot crew saved my life. This occupation has provided me structure, financial stability, and camaraderie. In return it has asked of me integrity and accountability. I spent the whole winter before that first season with dark ideas permeating my thoughts. Somehow, two weeks before critical I snapped out of it enough to show up and not quit. It was a tough start but I caught up and halfway through the summer I was walking around laughing with a saw on my back.
Currently it’s as if the dark portion of my mind that usually takes up 5%-20% has almost completely taken over. This part of my brain wants to break me down, call myself an imposter, and ultimately kill me. I am in sink or swim mode; I am trying to save my own life this time. It became clear as the season drew closer that I was not mentally prepared to be the high-functioning firefighter I usually am. I chose to draw back and focus on my personal life rather than risk becoming a liability on the job.
So often we think of our “work life” and “personal life” as being distinct and separate entities. I would like to express that this mentality is highly detrimental to the lives of employees. We cannot adequately perform our duties when there is such a rift between what we ask of firefighters and what we provide to them. Keeping your personal life separate is an old-guard means of avoidance. It also denies the possibility that our two lives can actually intertwine and complement each other. If we talk about the “fire family” and supporting our people, we cannot ignore the high numbers of individuals currently struggling.
In my fight against mental illness I am extremely and perhaps rarely privileged to have a supervisor who convinced me not to resign. I am further lucky that this person’s bosses trust them to make this call. Maintaining my health insurance is proving critical to my efforts at achieving wellness. This time off is not without consequence for me. First and most obviously, I am experiencing a drastic reduction in my usual income without roughly 1000 hours of overtime to bank on. I will miss out on months of on-the-job training and the professional development and networking that happens so fluidly in the field. Thus far my fancy federal health benefits have fallen short as my insurance company keeps rejecting my doctor’s efforts to get me the treatments I need. More personally still, I carry guilt and shame from not showing up this season, including a sense of failure from not exercising my skills and attributes alongside my coworkers.
One of my greatest fears when I consider my anticipated return to work is that people will find out. They will know I cracked. They may lose trust in my abilities; they may invalidate my strengths in light of my weaknesses. What will future potential supervisors say when they see I took an extended absence during what is sure to be a busy year in fire? I feel the weight of every destructive incident on my back, and I feel comfortable asserting that this is a common feeling. I do not however possess the mental capacity right now to worry about all that. I have made the selfish but necessary call to choose myself in this battle.
Droughts are deepening, climates are changing, and we always seem to work short-handed. If I am not alone in my mental health crisis, which I am not, how will we continue to effectively manage increasingly larger and more disastrous fires? I would argue that we should not go another shift without providing the support our people need. We must allow our wildland firefighters to show vulnerability in the face of so much global chaos, and seek to do the actual work it takes to remedy this. Furthermore, we need to collectively fight the deep-rooted professional and cultural stigma around mental health. Just as if it were a catastrophic fire we must fight aggressively and with great urgency.
Note from Bill:
Help is available for those feeling really depressed.
- National Suicide Prevention Lifeline: 800-273-8255. Online Chat.
- Anonymous assistance from the Wildland Firefighter Foundation: 208-336-2996.
- National Wildland Fire and Aviation Critical Incident Stress Management Website.
- Code Green Campaign, a first responder oriented mental health advocacy organization.
- A new organization, Fire Mind, will be dedicated to helping wildland firefighters and expects to be fully operational by June 30, 2021.
- Would you rather communicate with a counselor by text? If you are feeling really depressed or suicidal, a crisis counselor will TEXT with you. The Crisis Text Line runs a free service. Just text: 741-741