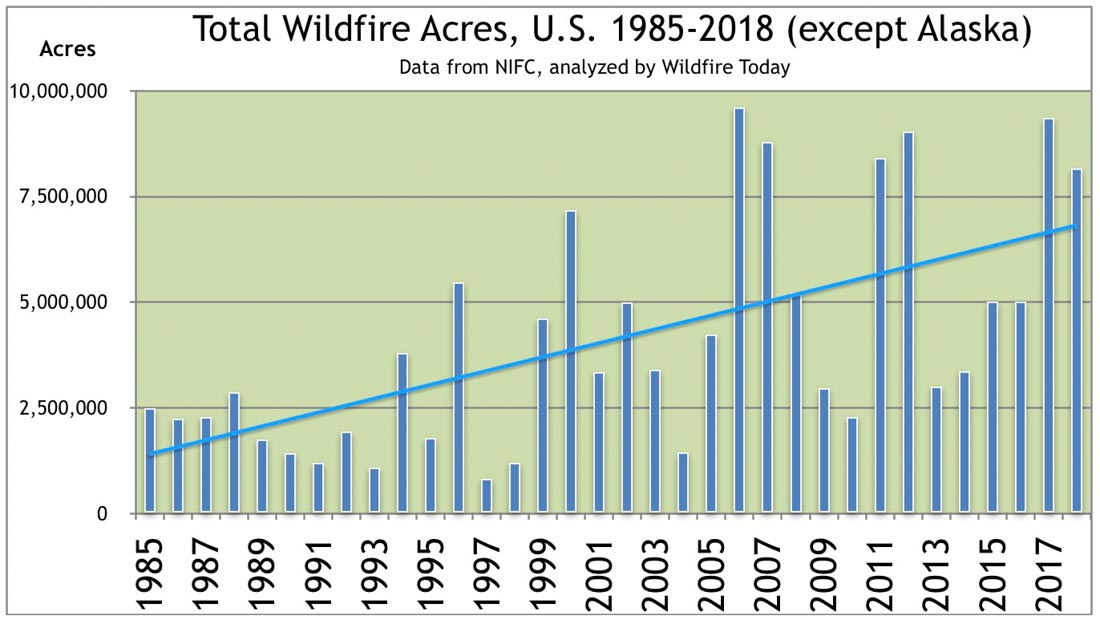
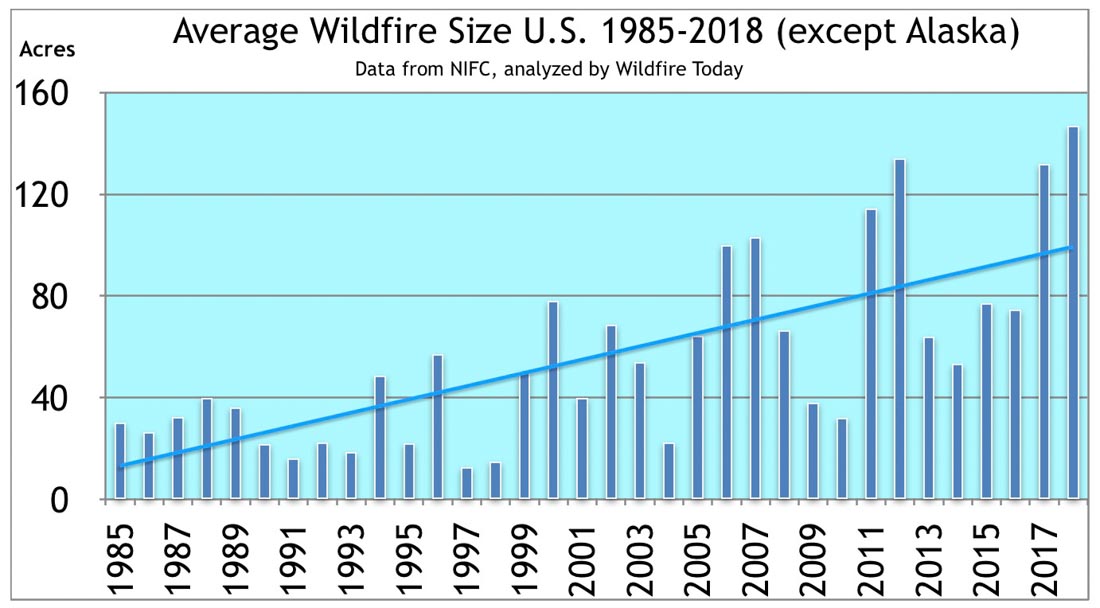
Chief John Hawkins shared with us a copy of the California Department of Forestry’s Fire Control Handbook, 1977 edition. The agency was known as CDF before they became the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection, CAL FIRE.
It is a .pdf copy of Handbook 5600 with a few amendments around 1979 and 1980 to address the agency’s limited trial of the Incident Command System (ICS) in their Region VI starting in 1978, and the planned California-wide implementation of the ICS in 1983. The entire document can be downloaded here (large 10.2 Mb file).
Firefighters of a certain age will most likely enjoy skimming through the pages of this 45-year old document.

The 324-page book contains many operational guides, as well as information about aviation, safety, pre-attack planning, “support teams”, and flood control operations. Much of it is timeless, but there have also been many changes. It is interesting to compare the 45-year old policies with current procedures.
But going back even further, let’s take a look at fire organizations before ICS began to be adopted in the 1980s:
- “Two-Sector Fire” organization from Principles of Organization for Forest Fire Suppression, US Forest Service, 1953, and,
- Organization that was used on the Battlement Creek Fire in 1976.
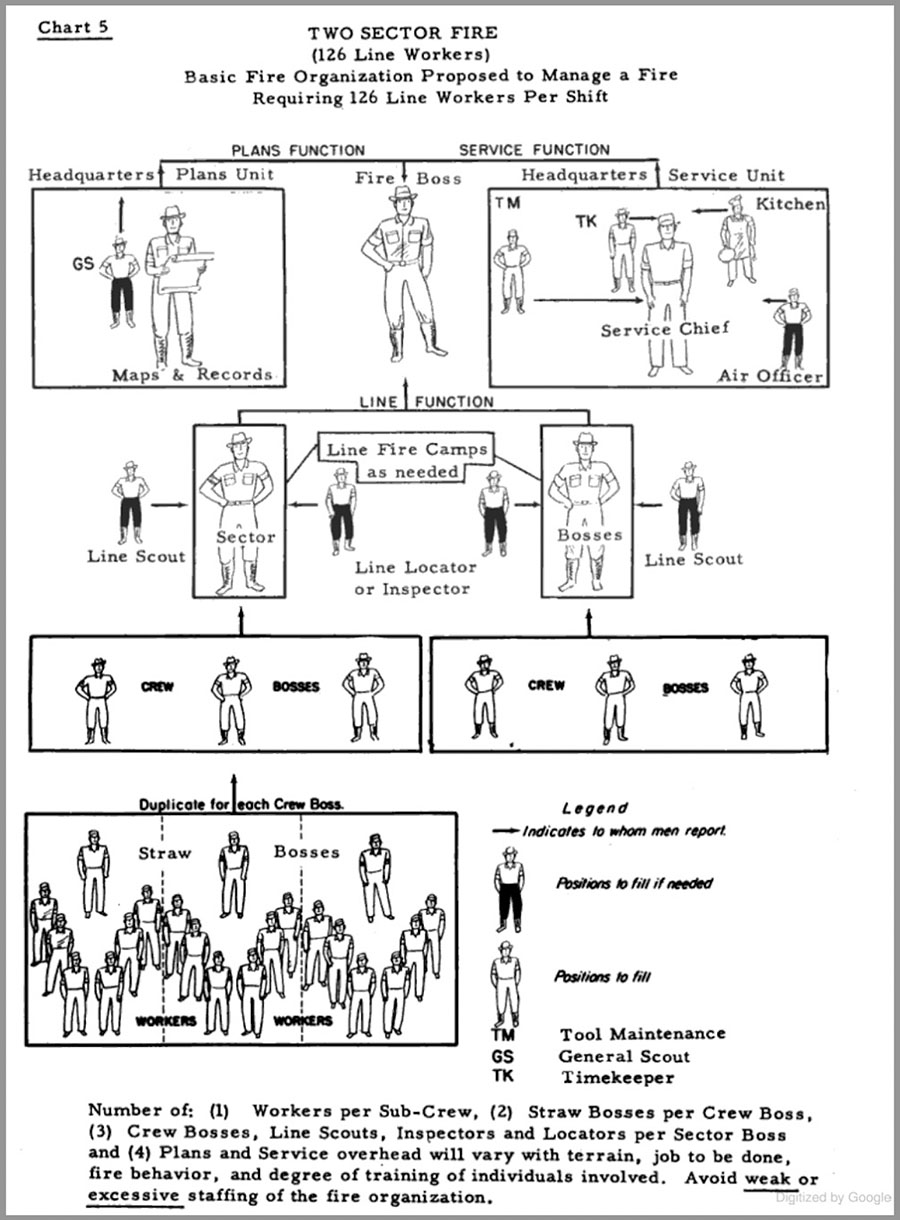
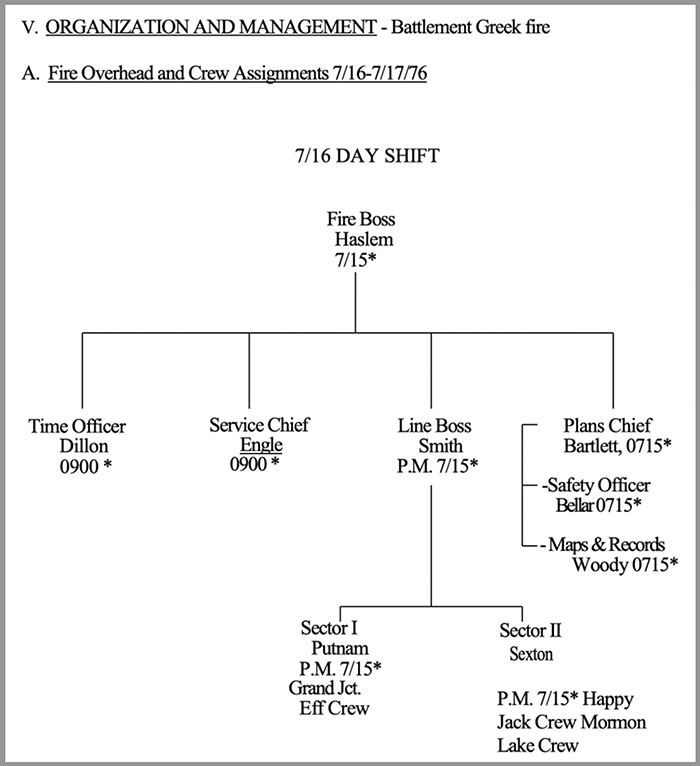
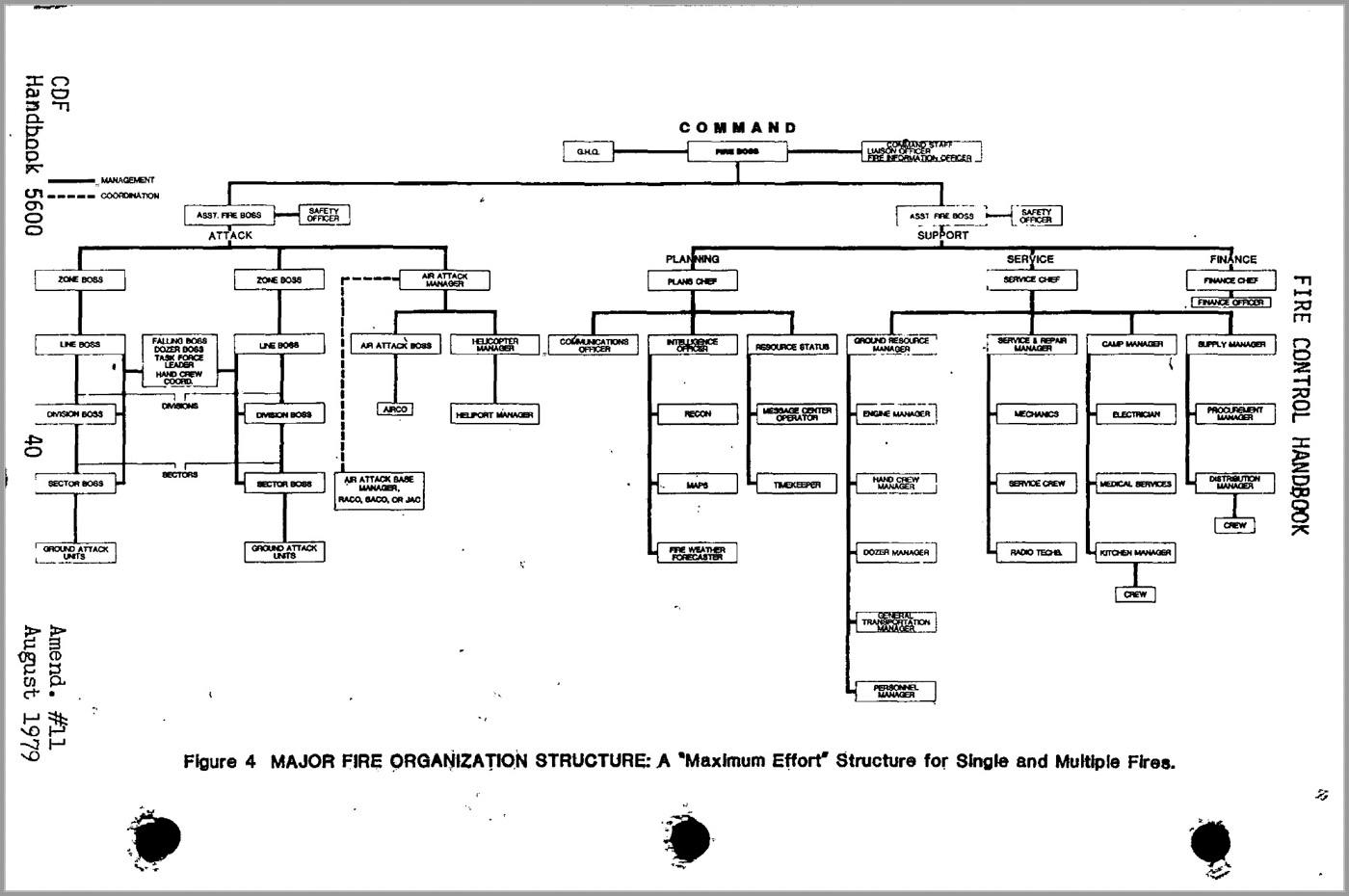
My career was with the US Forest Service and National Park Service. The CDF organization from the Fire Control Handbook has at least one feature unfamiliar to me, the “Attack” function, which was called the Line Function by the USFS. It is now labeled “Operations” in the ICS. In the USFS it was led by a Line Boss in the pre-ICS days. “Service” became Logistics, and in the Planning section the Maps and Records Officer was replaced by two units, Resources Unit and Situation Unit. Sectors became Divisions, and a new position was inserted between the Planning Section Chief and Division Boss: Branch Director. There were numerous changes in Service/Logistics.
And then there is the current Incident Command System structure; keep in mind, you only fill the positions that are needed.
Continue reading “Highlights from the 1977 CDF Fire Control Handbook”