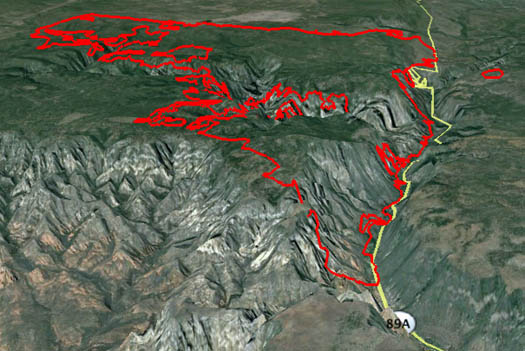
Forest treatments to reduce hazardous fuels made it easier to contain two wildfires in Arizona this year, according to Wally Covington, the director of the Ecological Restoration Institute, and a Regents’ professor of forest ecology at Northern Arizona University. In an op-ed at LiveScience, Mr. Covington said the fires had the conditions, and the chance, to burn hundreds of houses and destroy some of the state’s most coveted recreational tourist attractions, but they didn’t.
He is referring to the 21,000-acre Slide Fire and the 7,000-acre San Juan Fire which started in May and June, respectively. While they still grew into large fires, Mr. Covington said they could have become very damaging megafires, if not for the fuel treatments previously conducted on the Apache-Sitgreaves and Coconino National Forests.
Below is an excerpt from the article:
…The San Juan fire also provided lessons about how treated areas did what they were designed to do: slow a fire’s advance and restore a forest’s natural ability to self-regulate. How a wildfire behaves when it reaches a treatment area is a good test of how those treatments work. Fire crews and incident management teams reported that when the fire burned into areas that had been thinned, it burned with low severity and on the ground, not in treetops. The dry, frequent-fire forests of the West evolved with this type of fire, a slow-moving, low severity surface fire that would remove young trees and revitalize understory grasses and forbs. Anecdotal evidence from the San Juan Fire also suggests that the previously treated areas allowed fire crews to safely conduct burnout operations, thus enabling them to manage and control the fire.