
[DETAILS]

News and opinion about wildland fire
Federal firefighters have for years put up with both low pay — starting at just $15 an hour for entry-level positions — and a high-pressure job that takes a heavy toll mentally and keeps them away from their homes and families. Hundreds of them have left federal service, and hundreds more will likely leave next month if a permanent federal pay increase is not approved by Congress.
This fall, as reported by The Guardian, pay issues are coming to a head. A temporary pay increase, effected as part of Biden’s 2021 infrastructure bill, will expire at the end of September. Without that pay increase, the U.S. risks a crisis of firefighter burnout and falling retention while fires increasingly burn larger, hotter, and for longer than they have in decades.

Congress has two weeks to enact a long-term fix. If they fail, federal land management agencies may be left to navigate another mass exodus from the essential workforce just as autumn winds increase risks across the West.
As the Federal News Network recently reported, wildland firefighters are meeting with congressional leaders this week to add urgency to pending legislation that would install a permanent pay raise. The $600 million that funded the two-year pay boost runs out at the end of September.
Back in July, Grassroots Wildland Firefighters launched a petition to tell Congress what’s at stake if they don’t enact a permanent pay solution. In just a week, more than 11,000 wildland firefighters and others signed their names and described what will happen if Congress fails to act. A sample of signers’ responses:
“Firefighters don’t want accolades, they don’t need to be called heroes,” says Riva Duncan, a retired USFS fire officer and vice-president of the Grassroots Wildland Firefighters advocacy group. “But they want to at least be treated like they are appreciated for the risks they take and the sacrifices they make.”
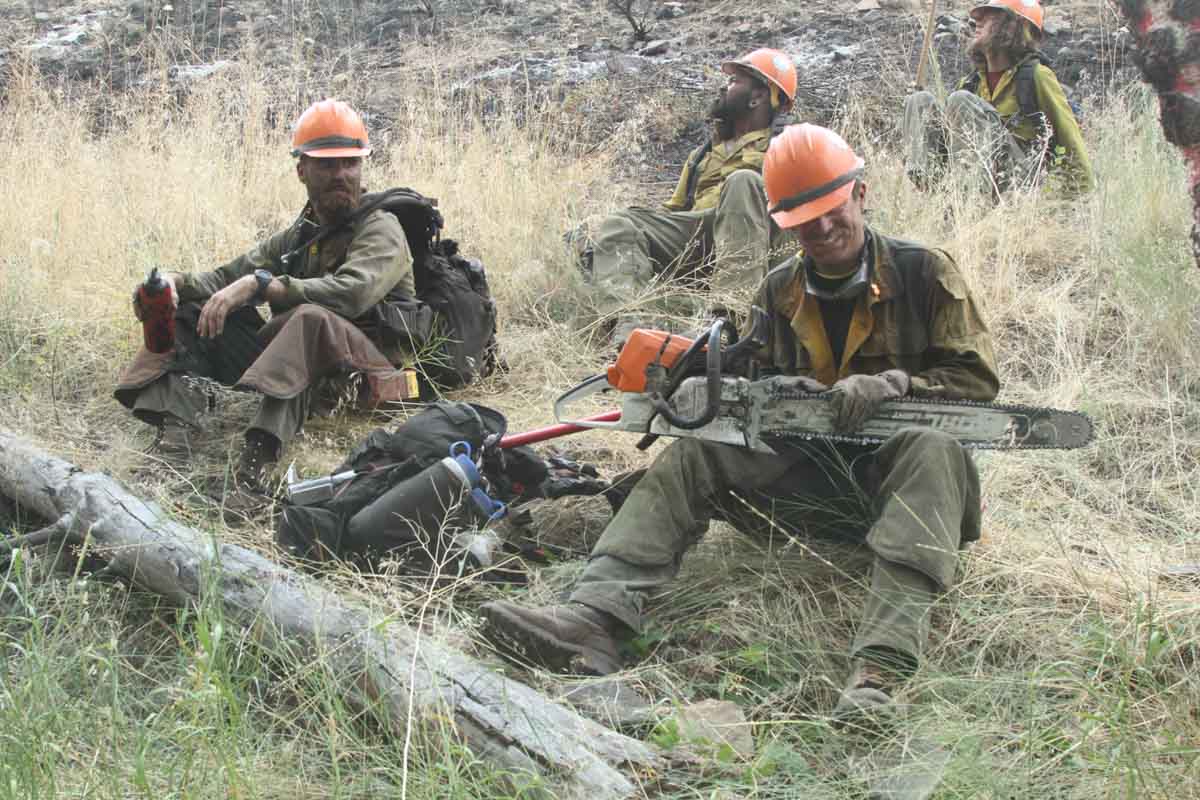

Biden’s temporary pay bump — which added either $20,000 or a 50 percent increase to firefighter paychecks, whichever was less — was intended as a short-term fix to buy Congress time to pass a permanent solution to the problems that have for years left federal firefighters underpaid and overworked.
The National Federation of Federal Employees, the union that represents many wildland firefighters, said without a permanent solution, there will be a “mass exodus” of firefighters, which would only exacerbate retention challenges that are already increasingly difficult for the four Department of the Interior agencies and the Forest Service; all five agencies employ roughly 17,000 wildland firefighters combined.
That story in the Guardian, by Gabrielle Canon, is WELL WORTH the read — and thanks to Nancy for the tip.
Without the passage of new legislation, federal firefighters will see major reductions to their paychecks starting October 1. Some workers’ pay will be cut back to $15 per hour. … California lawmakers, by the way, just passed a bill that would make $20 an hour the minimum pay for fast-food workers in the state. You can sign the Grassroots petition to Congress [HERE].
Nearing a congressional deadline, one bill is making its way through the nation’s legislature attempting to stop a tens-of-thousands of dollars’ reduction to wildland firefighter pay.
A previously enacted federal wildland firefighter pay increase is set to expire on October 1, an increase that would subsequently reduce firefighter pay by either 50 percent of their current salary or by $20,000, whichever was lower. This federal pay increase was first granted in August 2021 as part of the Biden Administration’s Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act of 2021, but the raise itself was only a temporary measure.
Without prompt action from Congress, federal firefighters are facing five-figure pay cuts next month.
A piece of legislation that has been introduced to Congress, the Wildland Firefighter Paycheck Protection Act (WFPPA), would stop the decrease from taking effect by permanently increasing wildland firefighter pay. This Act would authorize premium pay for federal firefighters portal-to-portal whenever they respond to a wildfire, prescribed burn, severity incident, or an incident that the Secretary of Agriculture or the Secretary of the Interior determines is similar in nature. Premium pay would not be paid to wildland firefighters during an initial response or initial attack fire if the wildfire is contained within 36 hours. If passed, the pay scale and premium pay regulation would take effect on October 1, according to the Congressional Budget Office.
The USFS employee union has warned that Cal Fire and other non-fed firefighter employers are anticipating that a third of federal firefighters could likely walk because they’re fed up with their paycheck uncertainty.
A similar bill was introduced to the U.S. House of Representatives in October 2021, but it never got past its introduction.

The Tim Hart Wildland Firefighter Classification and Pay Parity Act, named after a smokejumper who died while parachuting into the Eicks Fire in New Mexico earlier that year, would establish a pay scale that would increase yearly and institute hazard pay for wildland firefighters.
But the WFPPA, along with numerous other bills, is threatened by yet another pending government shutdown — if lawmakers can’t also allocate funding to the other 437 government agencies for this fiscal year.
In the event of a shutdown, thousands of federal workers would be furloughed without pay.

There were 11,187 wildland firefighters (GS-9 and below) employed through the USFS as of July 25, the agency says on its website. Funding proposed for the next fiscal year would reportedly support the hiring of 970 more firefighter positions, but Congress has to make that budget a reality.
“We struggle to hire and retain firefighters in areas of the country where the labor pool is low and pay isn’t as competitive as we would like,” they said. “Our goal is for firefighters to have a sustainable, long-term career that rewards them for the unique and hazardous work they do.”
The USFS is hoping to hire around 150 new firefighters in the Pacific Northwest and Alaska area. Interested in applying? Click here to see the positions’ full details.
The nation’s newest national monument has a long history of fighting off fire. Its future may mean defending its artifacts against firefighters.
The Baaj Nwaavjo I’tah Kukveni — the Ancestral Footprints of the Grand Canyon National Monument in northern Arizona — was formally designated in August. The monument land includes three areas to the north and south of the Grand Canyon and takes up approximately 917,600 acres, according to the Forest Service.
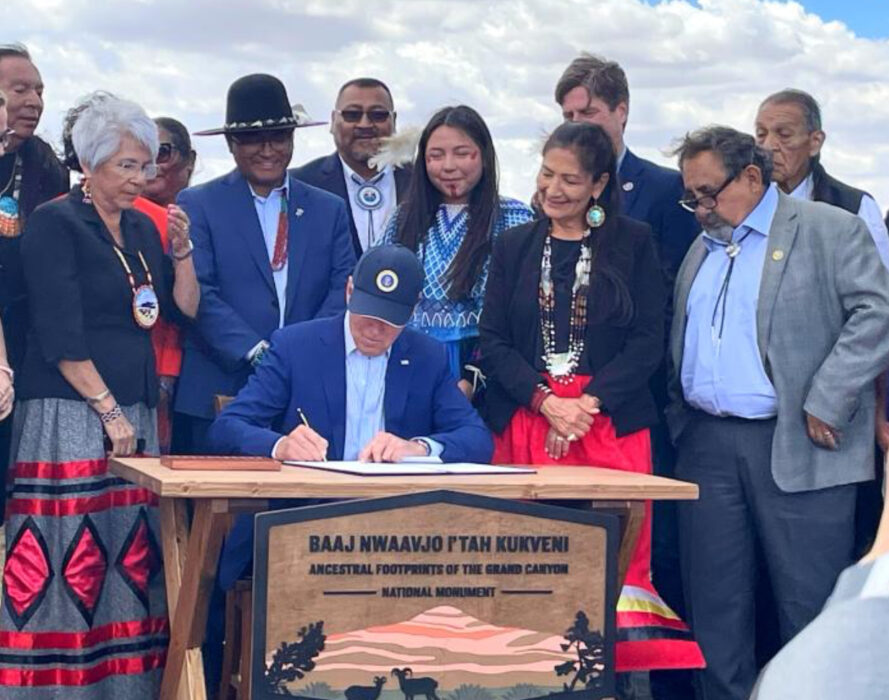

These lands are at the heart of many tribes in the region, including the Havasupai Tribe, Hopi Tribe, Hualapai Tribe, Kaibab Band of Paiute Indians, Las Vegas Paiute Tribe, Moapa Band of Paiutes, Paiute Indian Tribe of Utah, Navajo Nation, San Juan Southern Paiute Tribe, Yavapai-Apache Nation, Yavapai Prescott, Pueblo of Zuni, and the Colorado River Indian Tribes.
The tribes have called this area home for around 23,000 years, a history told through the numerous dwelling sites, pottery, and numerous other artifacts in the area.
Although a passing wildfire can damage artifacts, the fire itself isn’t often the main concern of the archaeologists in charge of protecting the monument. The cultural resources have existed in spite of the countless wildfires that have burned across the landscape, fires that subsequently give life to the Kaibab National Forest that surrounds the Grand Canyon. More often, archaeologists’ main concern is making sure the efforts of firefighters to contain a wildfire don’t put artifacts at risk.
“We’re not as concerned with the fire itself when fire-sensitive sites like wooden cabins and hogans are not present, but the tactics we often use to contain wildfire like constructing fuel breaks,” explained Michael Terlep, a district archaeologist for the North Kaibab Ranger District.
“The blade of a bulldozer, for example, scrapes the surface and disturbs at least the first six inches or more of topsoil, which might contain pottery, artifacts, arrowheads, tools, and prehistoric habitations. There is also the potential for ancestral burials to be disturbed.”
Terlep was one of the four resource advisors assigned to the Kane Fire that started on August 4 just north of the Grand Canyon. There, he was tasked with working ahead of crews, surveying the land, making sure fire suppression didn’t give way to cultural destruction.
“We were called immediately because anytime firefighting activities might disturb an archaeological site, we can be an asset, and advise on the best way forward,” Terlep said.

Resource advisors have been deployed to wildfires since the 1970s, according to NPS. However, increasing recruitment and training efforts for the positions have reportedly become a national priority for the agency.
In the past four years, 1,300 students from federal, state, tribal, and local agencies completed the NPS resource advisor training, NPS notes on its website. “This represents an increase of 125 percent compared with the preceding four-year period. Hundreds of the graduates went on to assist on wildfires and other emergency incidents as resource advisors and archaeologists .”
Interested in becoming a resource advisor yourself? Sign up to be notified when the NPS virtual introductory course for 2024 opens in the spring.
thehotshotwakeup.substack.com/p/a-california-nightmare
I’ve not verified this yet, but I will. Read more at the link.
15:25 UPDATE FROM THE IMT:
Neither the USFS update nor the Inciweb page makes any mention of this. But then the “Hotshot Wake Up” has no name or contact info attached to it. Anyone vouch for that “author” ?


And, two days later, an update:

Thanks to TS for the tip and to Bill Morse for the answers.
Several major insurance companies have stopped accepting California homeowners for new policies because of growing wildfire risks. As the number of fires in the state increases and other factors escalate, insurance companies worry about the risk — and the expense.
In 2022 there were over 5,000 wildfires, according to Cal Fire, that burned about 118,000 acres. Already this year 4,337 fires have burned over 114,560 acres.
Residents in high-risk fire areas or hurricane regions need homeowners’ insurance — and lenders require it. No insurance, no home loan. More people are moving into the interface, costing insurance companies too much to repair and replace houses while battling inflation, said Janet Ruiz with the Insurance Information Institute. Two insurance giants withdrew from California’s home insurance marketplace, explaining that increasing wildfire risk and soaring construction costs have resulted in their decisions to stop writing new policies in the state. State Farm announced last week it would stop accepting applications for all business and personal lines of property and casualty insurance, according to the Associated Press. The company cited inflation, a challenging reinsurance market, and rapidly growing catastrophe exposure.
“We take seriously our responsibility to manage risk,” State Farm said. “It’s necessary to take these actions now to improve the company’s financial strength.”
Unlike heavyweights State Farm and Allstate, which declined to sign new homeowners in the state, AmGUARD and Falls Lake will also drop their existing policyholders.
Allstate, another insurance powerhouse, announced in November it would pause new policies for homeowners, condos and commercial properties in California to protect current customers.
Homeowners may have to turn to the California FAIR Plan, which provides basic fire coverage, if they aren’t able to find an insurer that will cover fire expenses. The high-risk pool known as the FAIR Plan is not a government entity or a state program. Taxpayers do not fund the FAIR Plan — it’s supported by all carriers licensed to do business in California, which spreads the risk among all the insurance carriers. Because the FAIR Plan is a high-risk policy, people should expect to pay more than they would for a standard homeowner policy.
The San Francisco Standard reported last week that two more companies quietly left the California market, further narrowing options for those trying to insure their home or purchase one with a mortgage.
AmGUARD Insurance — a subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway GUARD Insurance Companies — will withdraw its homeowners and personal umbrella programs, and Falls Lake Insurance will also end its homeowners program. Both companies made the announcements July 21 in little-noticed filings submitted to the state regulator. AmGUARD and Falls Lake are the latest insurers to end or limit their business in the state during the past year.
Unlike heavyweights State Farm and Allstate, which declined to sign new homeowners in the state, AmGUARD and Falls Lake will also drop their existing policyholders. Safeco plans to drop 950 policies in October in San Francisco and the East Bay.
An SFGATE report noted that State Farm held the most policies in the California property market in 2021, and the company experienced about a 60 percent loss that year.