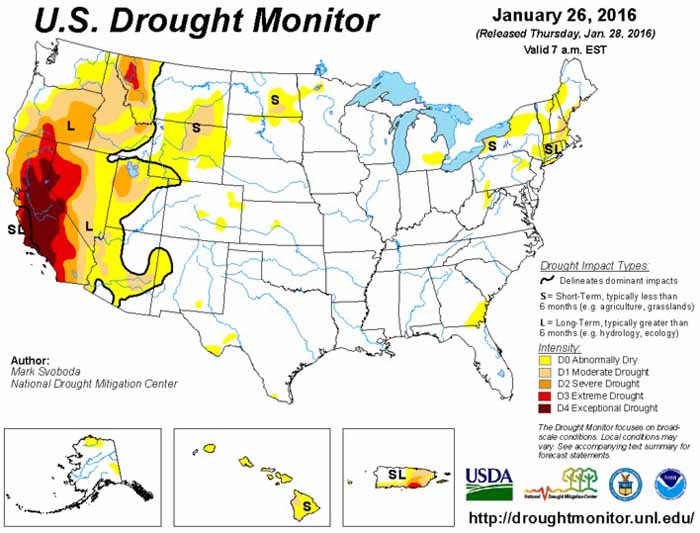
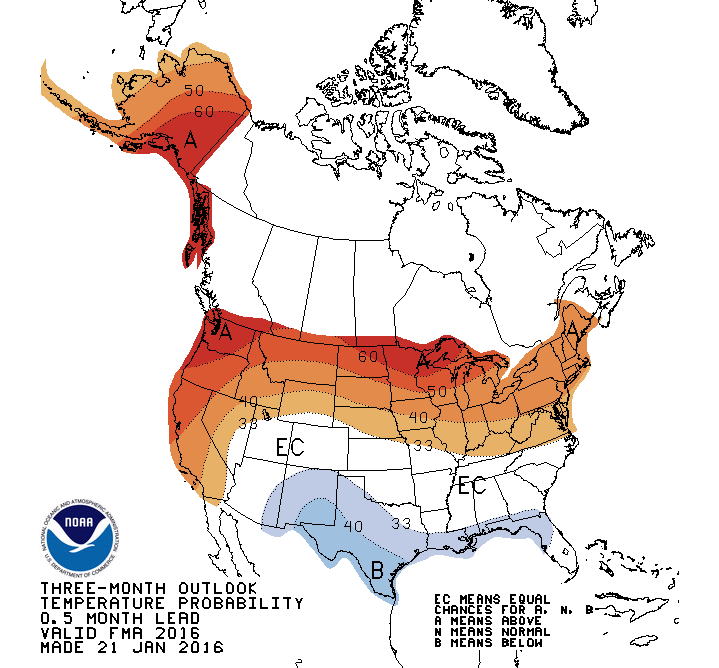
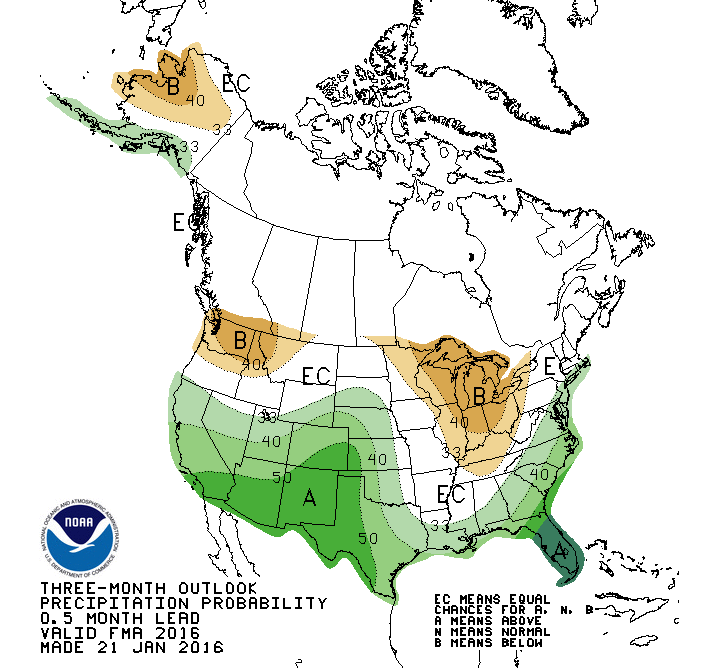
To interpret a wildland fire outlook can be a bit like posting a scenic photo to Instagram. You share the images and phases that capture the moment, with hopes that these will intrigue us into deeper connections to the months ahead.
AND THE RAIN AND SNOW FELL … From the latest National Significant Wildland Fire Outlook (for February through May 2013, with hints to the future), one image may lay claim to this month’s Instagram shot. The Total Precipitation Anomaly for January 2023 features a piercing finger of deep-green and blue anomalies from the central California coast eastward to upper Wisconsin – this being the precip falling from “multiple moderate to strong atmospheric rivers,” leading to moisture from 150 to more than 400 percent of normal.

What this means for fire potential long-term is to be determined. Though this was a wide and significant flow, it was not a universal flood. Wide areas are likely to remain in drought yet many regions, including northern California to Oregon and east into Idaho and Montana, are likely to improve, as depicted by the tan (improvement) and green (out of drought) shading in the U.S. Seasonal Drought Outlook through April.

WHAT TO EXPECT: The result of this precip is a fire potential outlook that is nearly Normal by May of 2023, with a slot of Above Normal red from west Texas to central New Mexico and a blob in the Georgia-Florida pinelands.

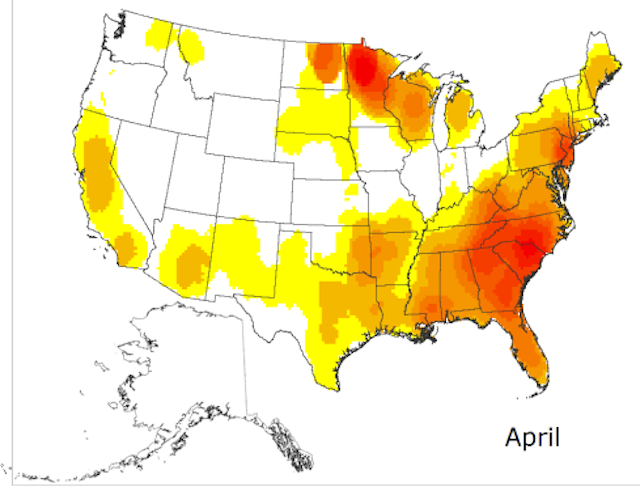
WHAT NORMAL LOOKS LIKE … in a typical season, for March into May, fires (including prescribed fires) may be relatively active on the land, particularly in the Southeast and southern Great Plans into the Trans-Pecos and Rio Grande, as illustrated in this map of normal fire activity for April.
Our tracking with “normal” will be influenced by global transitions as we’re likely leaving a record-long period of La Niña conditions. As the Outlook observes: “The Climate Prediction Center (CPC) is forecasting an 82% chance of neutral El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) conditions returning in spring. Other teleconnection patterns, such as the Madden-Julian Oscillation, Pacific Decadal Oscillation, Pacific-North American Pattern, and Arctic Oscillation are likely to influence weather and climate during the outlook period.” But we’re not through with the cool-ocean pattern yet: “La Niña is forecast to remain the dominant influence through February.”
So expect some variability to be foretold, as fuels grow into green-up and cure into summer.
For more, see the NIFC Predictive Services’ National Significant Wildland Fire Potential Outlook for February through May 2023.