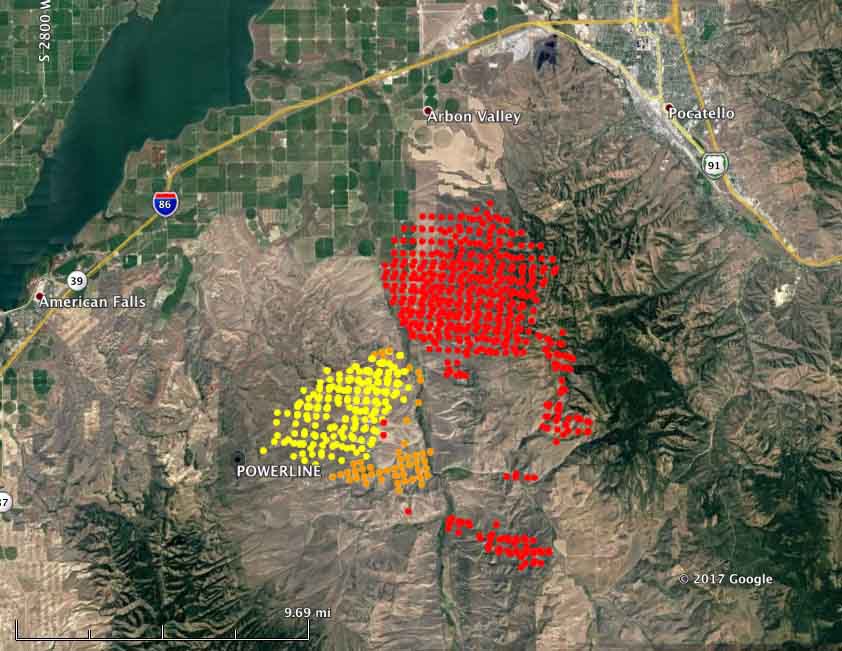
Above: A firefighter ignites a burnout on the Powerline Fire southwest of Pocatello, Idaho. Uncredited Inciweb photo, posted August 6, 2017.
(Originally published at 12:48 p.m. MDT August 6, 2017)
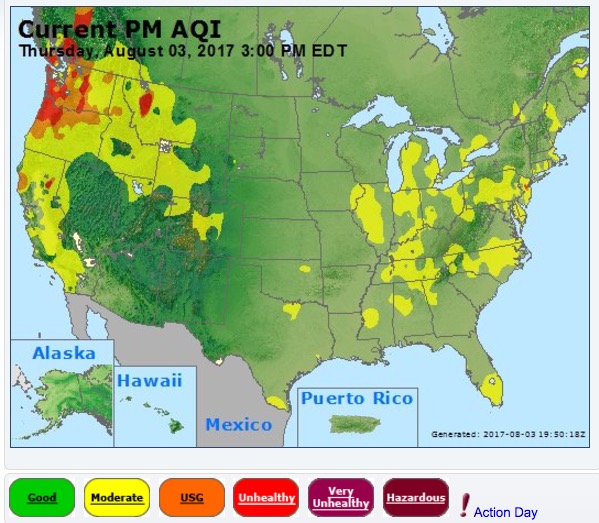
Wildland firefighters are much busier this year than in a typical year. To date, fires have burned 46 percent more acres than the 10-year average — 5,820,802 acres vs. the 3,962,906 average. In some years fire activity in Alaska, where many very large fires are not suppressed, can inflate these numbers, but so far that state can only account for 626,786 acres, not a huge number for Alaska.
400 hand crews, usually comprised of 20 people each, are deployed nationwide, along with 949 fire engines, and 120 helicopters for a total of 16,673 personnel.
Here are brief descriptions of some of the larger or more prominent fires:
- Powerline (see the map and photo above): Since it was reported Friday night this fire has spread very rapidly. Saturday it was very active on the northeast and southeast sides. Using satellite data the Incident Management Team estimated early Sunday morning that it had burned over 40,000 acres, but that is a very rough guess. More accurate mapping by fixed wing aircraft will provide better numbers. The satellite information indicated that by 4:04 a.m. Sunday it had spread to within 6 miles of Pocatello, Idaho. It is moving into steeper terrain with heavier fuels, offering more resistance to control and is the #2 priority in the Great Basin Geographic Area according to the national situation report.
- Mammoth Cave, southwest of Carey, Idaho. Since it started August 4 it has burned three structures and 30,000 acres. It is the number 1 priority in the Great Basin Geographic Area.
- The Shoestring Fire between Shoshone and Gooding, Idaho has blackened about 12,000 acres since it started August 5. It is the #3 priority in the Great Basin Geographic Area.
- The Rice Ridge Fire northeast of Seeley Lake, MT is the #1 priority in the Northern Rockies Geographic Area and is threatening over 1,000 structures. It added almost 700 acres on Saturday to bring the total to 7,740.
- The Sunrise Fire, 12,900 acres, the #2 priority in the Northern Rockies Geographic Area, grew by 600 acres Saturday. It has been burning since July 16, growing every day, adding several hundred acres daily on the east or northeast sides. It is now mapped at 12,900 acres.
- The Hanover Fire, in a very remote area 15 miles northwest of Riggins, Idaho, was extremely active on Saturday. The Incident Management Team reports that it has burned 4,479 acres.
- Parker 2, 10 miles east of Alturas, California. It was very active Saturday, adding 5,300 acres, growing to 7,100 acres.
- Minerva 5, just south of Quincy, California. It has burned 4,088 acres and the voluntary evacuation of the town has been lifted. Firefighters completed a firing operation Saturday night.