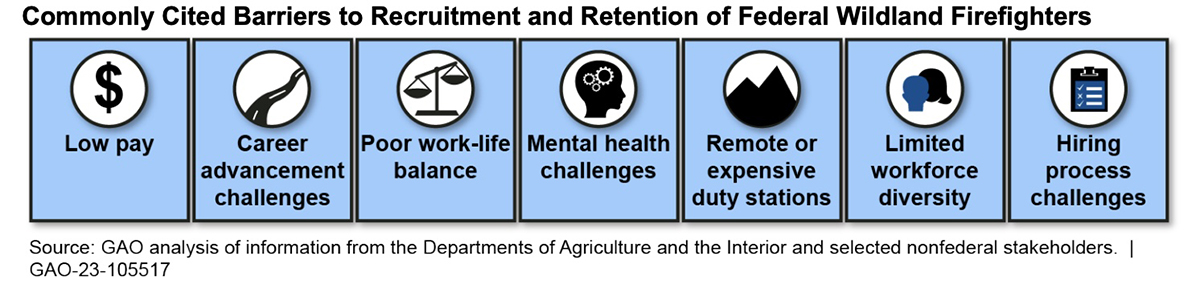
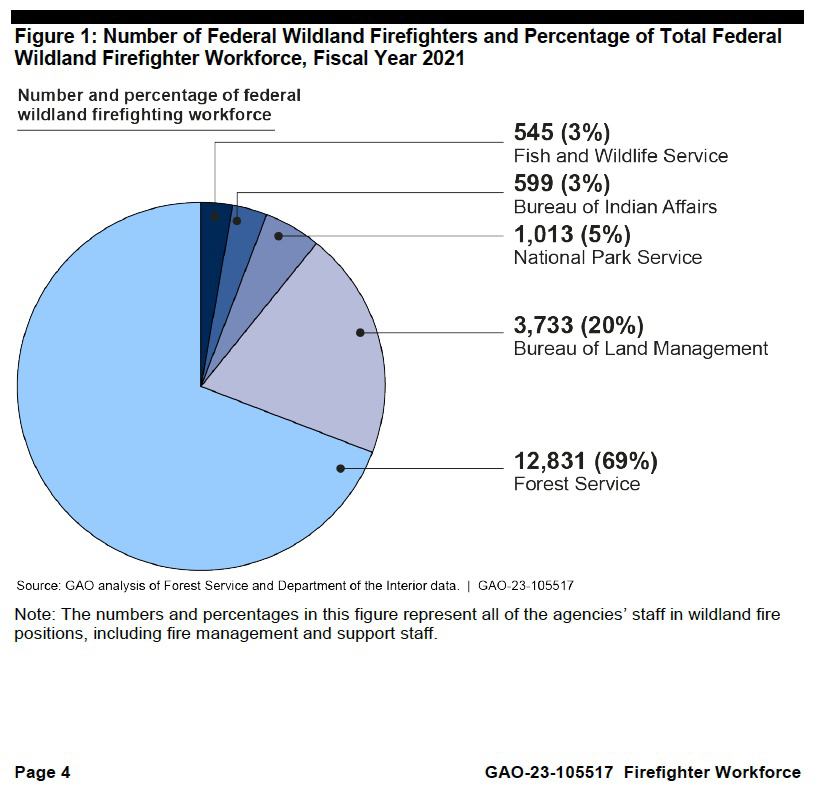
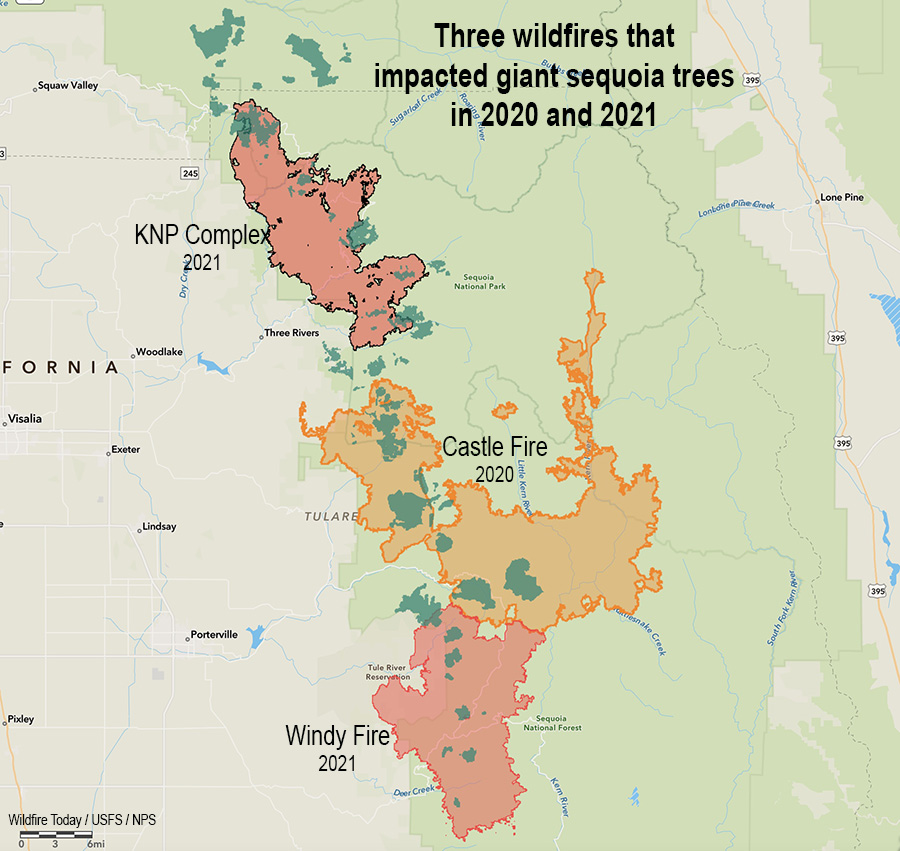
More than 2,000 applicants wanted to be a part of the British Columbia Wildfire Service in 2024, the highest number of applicants the service has seen in the past decade. The agency told WildfireToday that the application boost was linked to feedback received from the Expert Task Force on Emergencies established last October by BC Premier David Eby after the province’s historic 2023 wildfire season. The task force issued 31 recommendations, some of which were enacted swiftly ahead of the 2024 wildfire season.
Fire management made numerous enhancements to the Service’s wildland firefighter recruitment and hiring process as a result of the recommendations. Upgrades included expanding First Nations boot camps, extending the hiring period for new recruits, and encouraging applicants to indicate their work location preference.
The Service directly attributed the improvements to their having a full staff of 162 Initial Attack Crews and 30 Unit Crews in 2024, compared with the 149 Initial Attack Crews and 30 Unit Crews in 2023. Approximately 1,300 fire crew positions are employed directly with the Service, including an additional 500 permanent staff and 300 seasonal positions; 250 new recruits were invited by the Service from its New Recruit Boot Camps and First Nations Boot Camps this spring. The provincial 2024 budget provided $38 million to support stable, year-round staffing, including fire crew leaders and frontline staff who work in structure protection, prevention, risk reduction, and wildfire land-based recovery.
“People living in First Nations, along with rural and remote communities bear a disproportionate impact from the rising threat of wildfires,” said Wayne Schnitzler, task force member and executive director of First Nations’ Emergency Services Society. “I’m pleased to see the Province is boosting recruitment initiatives, including expanding First Nations boot camps as recommended by the Premier’s expert task force on emergencies. These initiatives break down barriers and pave the way for increased participation of Indigenous peoples as wildland firefighters.”
Apart from hiring, the Service said it will continue to implement numerous task force recommendations through 2024, including:
-
-
-
- Launching a wildfire training and education center at Thompson Rivers University
- Increasing new technology use to predict wildfire movement and growth
- Increasing community evacuee support funding
- Increasing the volunteer pool to support evacuees
- Boosting wildland firefighting fleet and equipment
- Enhancing wildfire recruitment tactics
-
-
BC Wildfire Service airtankers, meanwhile, are conducting practice flights from Kamloops and Penticton airports in the afternoons. The BCWS said airtankers out of Kamloops are flying the east side of Adams Lake, and the Penticton aircraft will conduct practice about 40 nautical miles east of Penticton.
CastanetKamloops.net reported that BCWS noted the exact location and timing of tanker practices are subject to change depending on weather and other conditions; the practices don’t involve active fire. After six days with no flying activity, practices are run to make sure aviation teams are ready to respond. “It is important for air attack officers and pilots to practice, as it allows them to remain proficient and prepared to respond to active wildfires,” BCWS said. “Practices also ensure the aircraft are mechanically sound and ready to respond.”