When the US Forest Service Deputy Chief of State and Private Forestry testified before members of Congress on April 5 that a firefighter hiring event “went very well”, the event had not started yet.

“We just completed an additional fire hire event in California at the end of March and those numbers are still coming in,” Ms. Jaelith Hall-Rivera said. “I do think we are on pace. By all accounts that hiring event went very well. Importantly what we are seeing is a very high acceptance rate in our permanent and seasonal permanent firefighting positions, which is what we want.”
In an article published today, Brianna Sacks of BuzzFeed News reported that the hiring event actually began April 11, six days after Ms. Hall-Rivera’s testimony, and is scheduled to go through April 29.
Ms. Hall-Rivera’s statement was in response to a series of questions from Rep. Katie Porter from California. You can watch this exchange in the video of the hearing we posted April 5 as part of a summary of the testimony before the House Subcommittee on National Parks, Forests, and Public Lands. Rep. Porter’s excellent questions begin at 138:35.
Below are excerpts from the BuzzFeed article:
A Forest Service spokesperson told BuzzFeed News that the deputy chief made an “error” because she “didn’t have all the information in front of her.”
“There are several hiring events throughout the year, and I think she was thinking of a different one in a different region,” the spokesperson said, but he did not provide specifics as to which one that might have been. The spokesperson also did not have hiring numbers that might back up Hall-Rivera’s assurances.
Interviews with firefighters in Colorado, New Mexico, Oregon, Washington, and California, as well as internal communications, hiring data, org charts, and surveys from the nonprofit Grassroots Wildland Firefighters, also tell a different story.
For example, in a Feb. 15 meeting hosted and attended by senior Washington officials, fire directors from across the US shared their issues with hiring, according to meeting notes obtained by BuzzFeed News. In New Mexico, where fires are currently raging, leaders said multiple hotshot crews would not be fully staffed. In the Pacific Northwest and Alaska, leaders said there is a “lack of candidates” and they are “unable to staff seven days in many places.” There is a “continued decline of folks to do the work.”
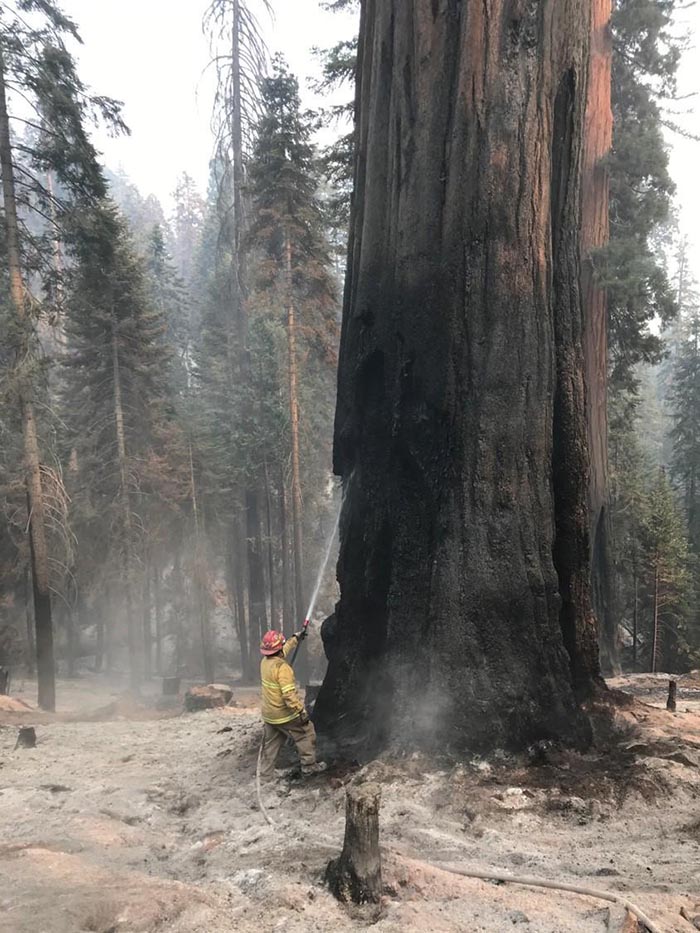
As California, Oregon, Utah, Washington, and Colorado gear up for fire season, interviews with three Forest Service employees familiar with hiring say the situation is grim. Without a serious staffing push, engines will sit idle, helicopters won’t be able to fly daily, crews won’t be able to start the season on time, and those who have worked multiple seasons in the field aren’t sure how much more they can stretch themselves without falling apart, they said. The Thomson Reuters Foundation, which also recently investigated systemic staffing issues, highlighted retention issues due to pay and housing.
In parts of Montana and Idaho, which had 700 seasonal workers last year, only 460 have returned for this fire season, a source familiar with the numbers said. And after last year’s Fire Hire, California had filled only 56 of 781 open positions, according to data obtained by BuzzFeed News. As of April 8, two days before this year’s hiring push, California had more than 1,560 vacancies, according to a review of the state’s openings.
More and more articles like this are being published documenting the hiring and retention difficulties that face the US Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management.
From Thomson Reuter Foundation News, April 25, 2022:
An engine captain involved in temporary hiring in northern California indicated that almost all Forest Service forests in the area expected to have less than 65% of full staffing for firefighters this year, some below 50%, according to a federal firefighting source who spoke on condition of anonymity.
“Fundamentally, people don’t want to take jobs because they can’t find a place to stay,” [Kelly] Martin [of the Grassroots Wildland Firefighters] said.
One female wildland firefighter – who lives out of her camper in California to save on rent – said proposals to increase base pay would not make up for the lack of an attractive career path for more experienced firefighters.
“Just raising the wages for those coming into fire is not going to be enough to keep people around,” she said, asking not to be named.